Hello,
There are 3 questions about the MUX.
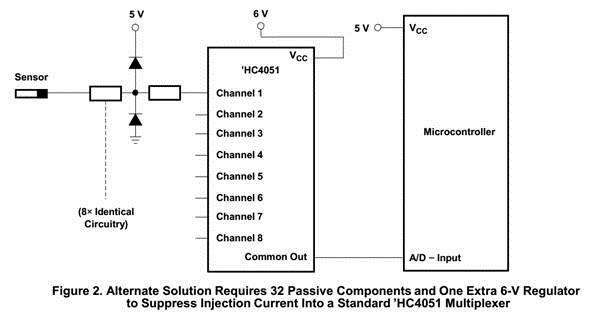
1. Do you know which field strength level of BCI and RI CD74HC4051 can satisfy? Currently, the signals through MUX are disturbed when our ECUs with CD74HC4051 perform BCI(Bulk Current Injection test) and RI (Radiation Immunity test).
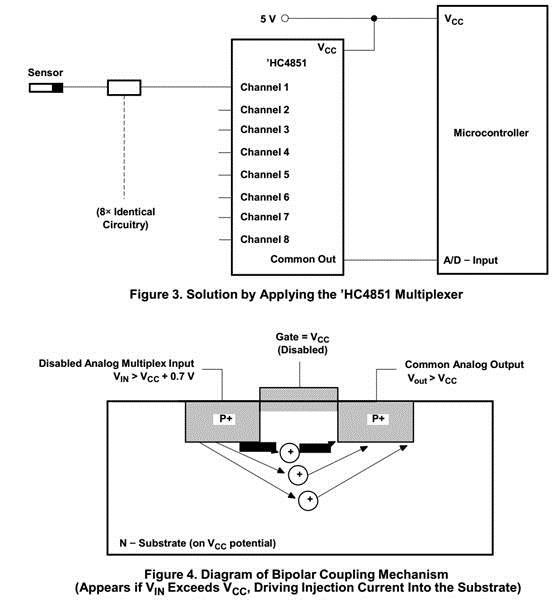
2. Another MUX “SN74HC4851-Q1” has good performance against BCI and RI, since injection current control is implemented for “SN74HC4851-Q1”. Do you know the detailed difference of CD74HC4051QPWRQ1 and SN74HC4851-Q1.
3. Could you also help to explain the mechanism of injection current control in SN74HC4851?
Thank you very much.
Bell