Hi,
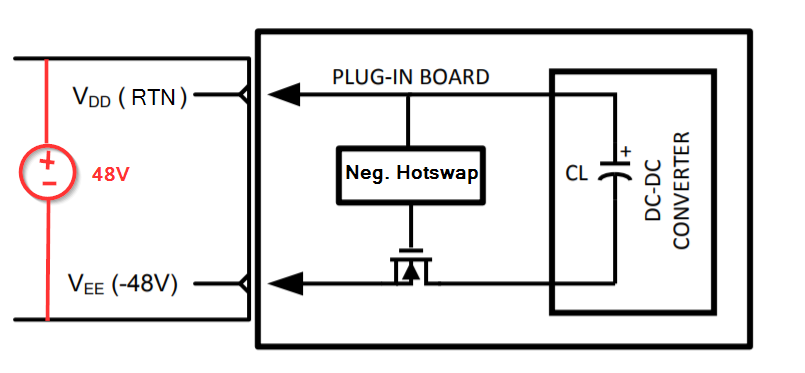
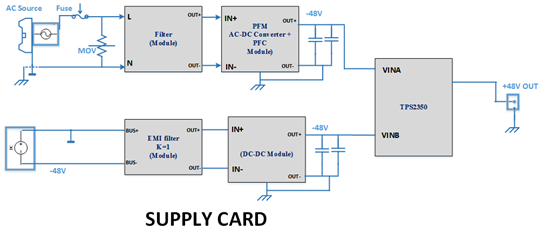
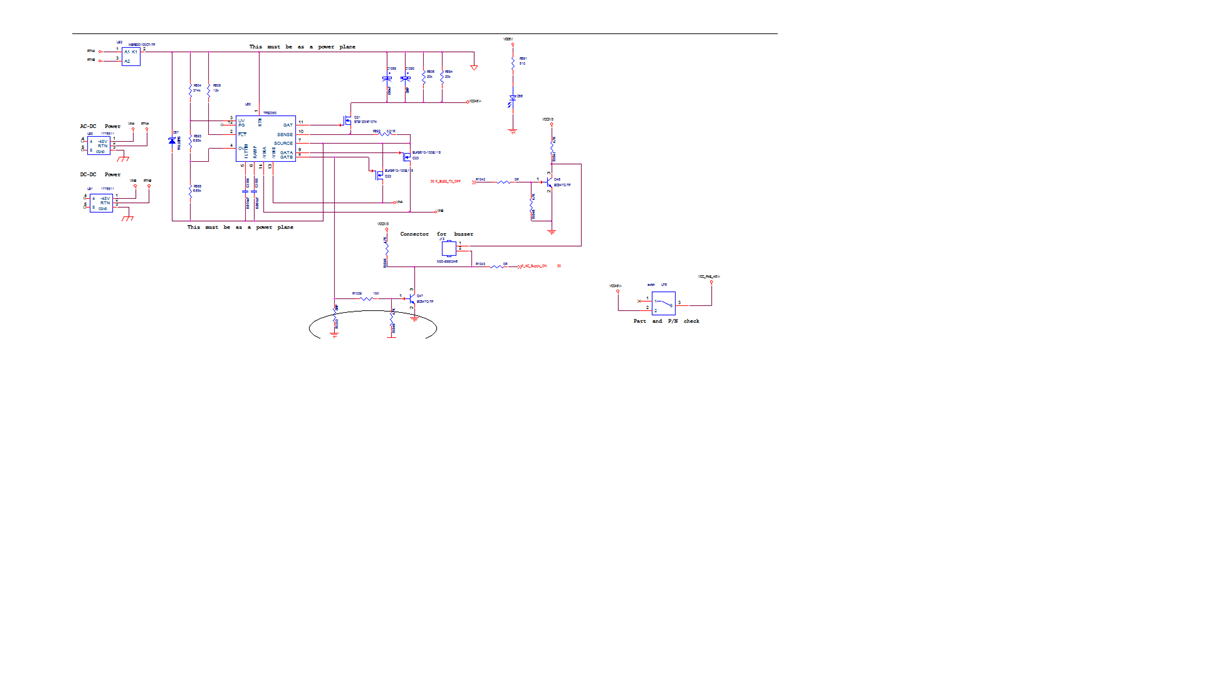
In our system there are two power supply one is AC to DC ( AC to DC -48 V)
In other Power supply Dc to DC ( DC is -48 Volt )
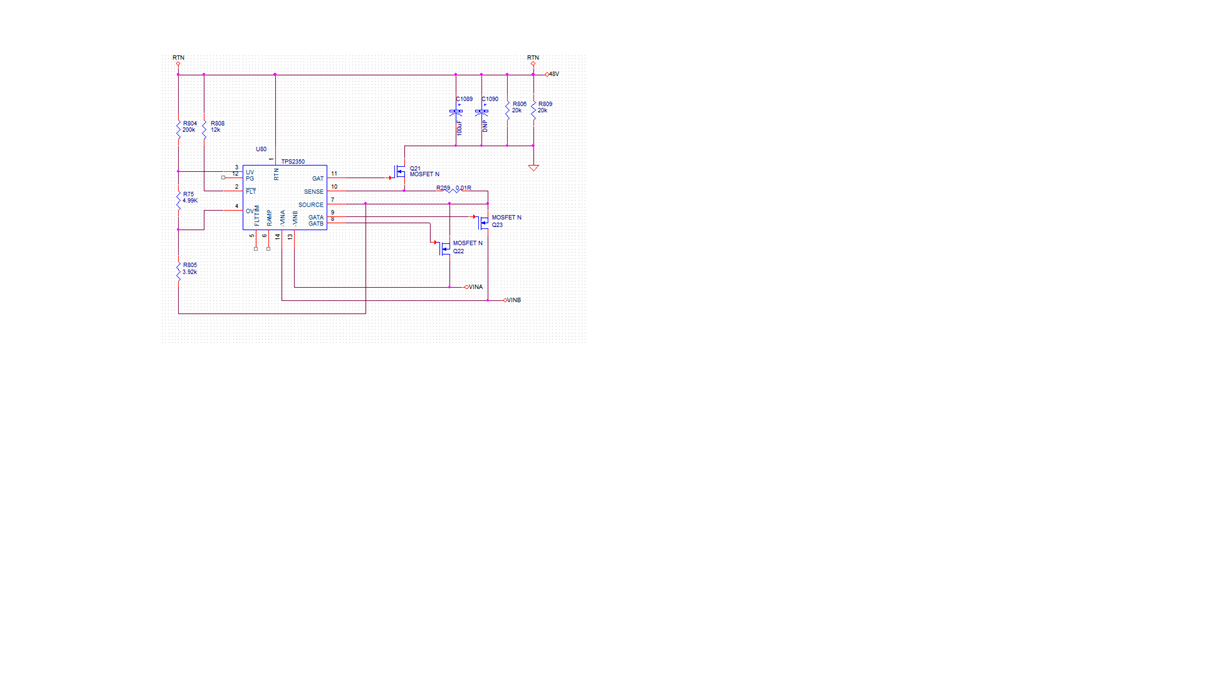
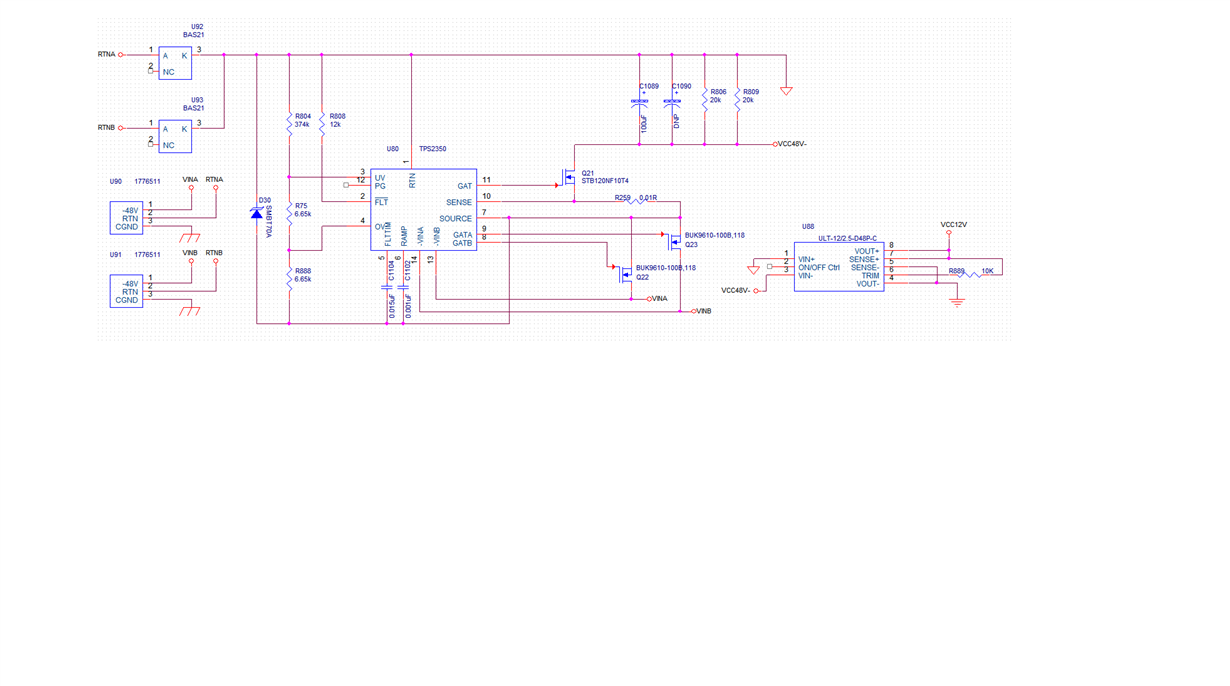
at a time only one supply is active, either supply coming from AC to DC board or from DC to DC board. We are using TPS2350 for both the supply , We are confuse input is -48V and we required output to +48 V can it be possible with this chip or we will get output only -48V.Please suggest reference schematic for this.
Regards
Neelam