A common requirement in battery-powered applications like metering, handheld or wearable products is to know the charge level of the battery. With this information, the system MCU can estimate the runtime and signal when the battery needs replacing or recharging.
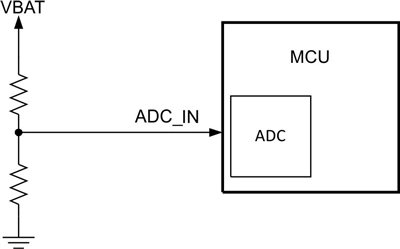
The easiest way to get the status of the battery is to feed the battery voltage into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and process the data. Scaling down the battery voltage to match the ADC input range requires an external resistor divider. Figure 1 shows a simple implementation.
Figure 1: A resistor divider scales down the battery voltage to the ADC input range
With a battery voltage of 4.2V and resistor values of 1.5MΩ and 470kΩ, the maximum ADC input voltage is 1V. The current through the resistor divider will be in the range of 2µA. This is about the same as the operating current of a MCU in low-power mode and can therefore have a strong reduction on your battery runtime.
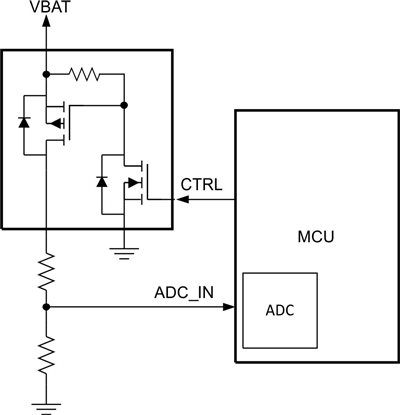
To avoid these additional losses due to the current through the resistor divider, you can use a switch to connect the resistor divider and the ADC input to the battery only when you need a measurement. A p-channel is typically the switch, with an n-channel MOSFET used as the level shift to drive the p-channel. With this configuration, an output of the MCU controls the switch.
Figure 2 shows the basic block diagram of such a discrete implementation consisting of a switch, resistor divider and low-power MCU with integrated ADC.
Figure 2: Adding a level shifter to reduce the current
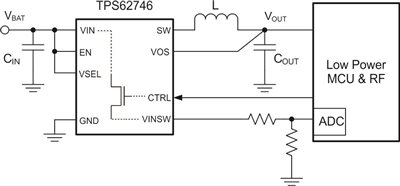
In battery-powered applications where you need the longest lifetime, you must also step down the battery voltage to an appropriate level to supply the MCU. This results in lower average power consumption of the MCU and increases the battery’s operating runtime. With its ultra-low quiescent current and integrated VIN switch, the TPS62746 buck converter is a good fit for such applications. The input-voltage switch is an integrated transistor that connects the battery voltage to a separate pin. The switch is easily controllable by using an output of the MCU to toggle a control pin.
The integration of switch and level shifter, which comes in a single SC-70 package, saves about 4mm2 of PCB space and cost compared to a discrete solution.
Figure 3 shows the TPS62746. Its integrated VIN switch enables a connection between the battery voltage and the ADC.
Figure 3: TPS62746 with integrated VIN switch
What designs are you looking to reduce leakage current in?
Additional resources
- Read these related blog posts from my colleague Chris Glaser: