Choosing the right audio op amp in different contexts:
Parts discussed in this thread: OPA167x,OPAx134,OPA165x,OPA1622,OPA160x,OPA1692,OPA1611,OPA1632,
With so many different audio op amps available from TI, it can be difficult to determine which one is right for you. The next section will focus on choosing the right audio amplifiers based on the application and end equipment. Keep in mind that audio amps are just one part of the audio channel as a whole. Every audio amplifier will almost always need to connect to data converter (DACs, ADCs, CODECs), which TI also makes.
Aftermarket Head Units
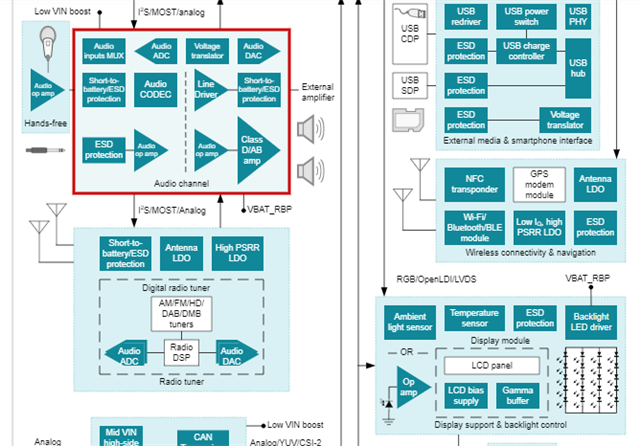
Figure 1: Reference design for aftermarket head units:
Aftermarket head units display most infotainment features in one system making them cost effective and easy to install for the original equipment manufacturer. Audio amplifiers will be needed whenever you are using the hands free communication microphone in the car to translate voice commands into functions. Audio amplifiers will also be found within the audio channel where digital and analog signal conversion is found to be translated to loudspeakers in the vehicle.
The purpose of the audio amplifier seems to match the need for low distortion and noise but also be able to propagate signals quickly and effectively.
|
Device |
Supply Range (V) |
Channel Count |
GBW (MHz) |
Noise at 1KHz nV/√(Hz) |
THD in dB |
|
Cost effective |
4.5 – 36 |
1,2,4 |
16 |
4.5 |
-120 |
|
True-FET |
5 – 36 |
1,2,4 |
36 |
8 |
-122 |
|
Lowest noise and distortion |
4.5 – 36 |
1,2 |
53 |
4.3 |
-131 |
Table1: Audio amplifier recommendation for aftermarket head units
For more information and other useful resources, take a look at the following content:
Aftermarket head unit reference design
Single-Supply Electret Microphone Preamplifier Reference Design
Understanding Op Amp Noise in Audio Circuits
Pro Microphones and Wireless Systems
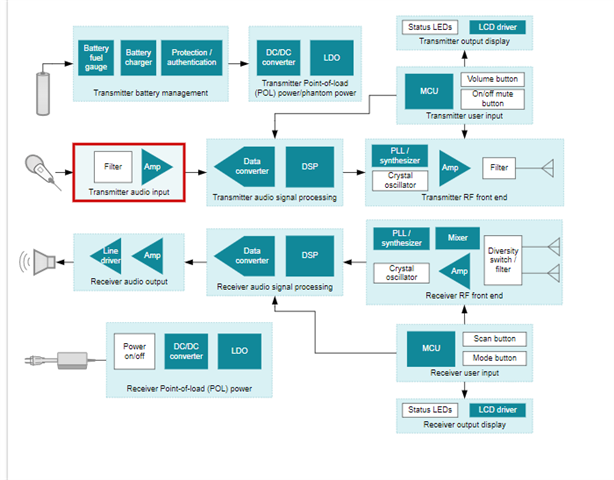
Figure 2: Professional microphones and wireless systems reference design
Professional Microphones and wireless systems need to deliver excellent audio quality with minimal noise and total harmonic distortion. In addition, the integrated circuits used must have low power consumption to ensure maximal battery life. Finally, the amplifier chosen must be have a small footprint to fit onto a wireless microphone's constrained PCB.
The amplifier size will vary based on the package that is chosen. Outside of that, audio amps within professional microphones and wireless systems will be primarily in charge of preamplification and signal conditioning. Therefore it is important that these amplifiers have low noise and distortion as well as low quiescent current to decrease battery consumption. Below you can see a table for three possible devices to choose from.
|
Device |
Supply Range (V) |
Channel Count |
GBW (MHz) |
Noise at 1KHz nV/√(Hz) |
THD in dB |
Iq (mA per channel) |
|
High performance |
4 – 36 |
2 |
32 |
2.8 |
-135 |
2.6 |
|
Balanced |
5 – 36 |
2,4 |
35 |
2.5 |
-130 |
2.6 |
|
Cost effective |
3.5 - 36 |
2 |
5.1 |
4.2 |
-127 |
.65 |
Table 2: Audio amplifier recommendations for professional microphones and wireless systems
For more information and other useful resources, take a look at the following content:
Professional microphone and wireless systems reference design
Soundbars
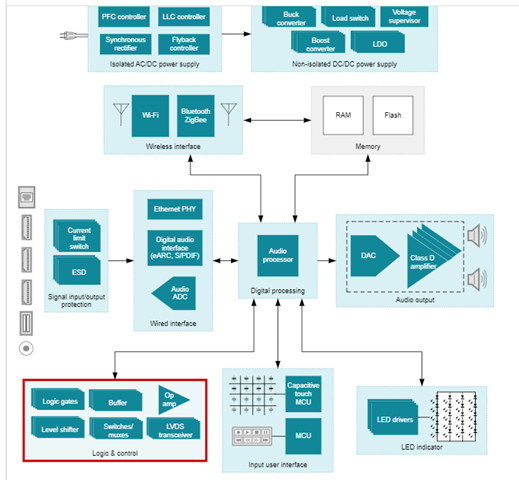
Figure 4: Soundbar reference design
Sound bars boast excellent audio quality, connectivity and low power consumption. Audio amps in relation to sound bars are normally found in logic and control interfacing with processors and data converters. In this way signal conditioning and translation matters most, so we want to be as precise as possible while having high speed and low noise and distortion. Because of this, we want to make sure that the offset voltage is down to a minimal as to not translate error.
|
Device |
Supply Range (V) |
Channel Count |
GBW (MHz) |
Noise at 1KHz nV/√(Hz) |
THD in dB |
Vos (mV) |
|
High performance |
4 – 36 |
2 |
32 |
2.8 |
-135 |
0.5 |
|
Balanced option |
4.5 – 36 |
1,2 |
53 |
4.3 |
-131 |
1 |
|
Cost effective |
4.5 – 36 |
1,2,4 |
16 |
4.5 |
-120 |
2 |
Table 3: Audio amplifier recommendations for soundbar logic and control
For more information and other useful resources, take a look at the following content:
Video Conference Systems
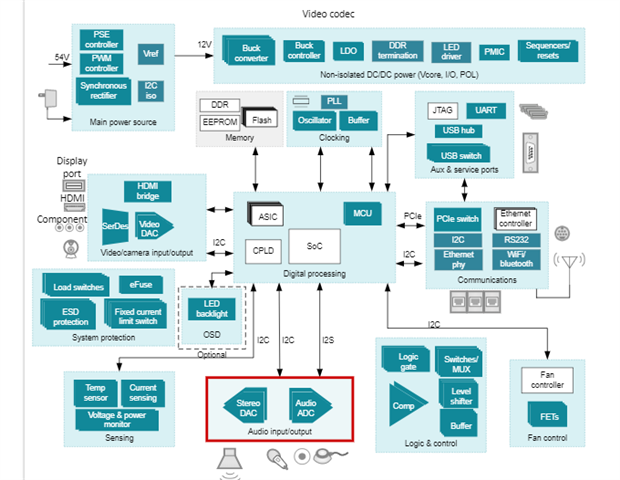
Figure 5: reference design for video conference system
From an audio perspective, video conferencing systems need to have the lowest noise and distortion parameters for audio to be conducted and received effectively. In addition, the amplifier needs to be high speed to accommodate different video formats, codecs, and specifications.
Speed is a key concern for video conferencing systems, so we want an audio amp that has a high slew rate as well as a high gain bandwidth. However, in the same vein as before, we want to minimize noise and distortion as much as possible to deliver the best audio quality. Below are some great options for this application.
|
Device |
Supply Range (V) |
Channel Count |
GBW (MHz) |
Slew Rate (V/us) |
THD in dB |
Noise at 1KHz nV/√(Hz) |
|
High Performance |
5 – 36 |
2 |
40 |
27 |
-135 |
1.1 |
|
Fastest |
5 – 30 |
1 |
180 |
50 |
-133 |
1.3 |
|
Cost Effective |
4.5 - 36 |
1,2,4 |
16 |
9 |
-120 |
4.5 |
Table 4: Audio amplifier recommendation for video conference systems
For more information and other useful resources, take a look at the following content:

