Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TLV7011, TLV1805
Hi team,
My customer is using this device as below,
- Monitor the power level of 5V, and the power supply for LM239 is +/-12V;
- The output is pulled up to 3.3V with 4.7k resistor;
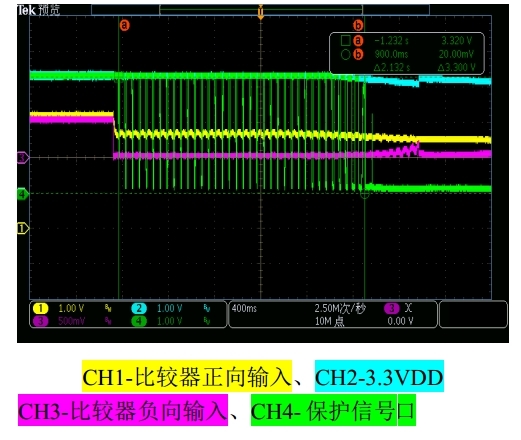
- One thing is that the 12V will power off first than 5V, and they can detect fault signal at the output; See waveform below.
They are curious about when the power voltage of LM239 is lower than 2V, such as 1V. Vp>Vn, what is the output voltage of LM239? Thanks.