Hi Team,
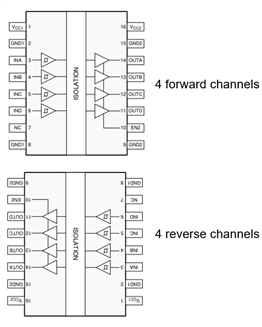
I am using ISO7740FQDWQ1 in my design. My requirement is to have Two 4 channel isolators of one with 4 forward channels and other with 4 reverse channels. But ISO774x-Q1 family doesn't not have 4 reverse channels configuration part. Is there any alternate part with 4 reverse channels configuration with similar features of ISO774x-Q1 (AEC-Q qualified) ?
--
Regards,
Kiran