What is ESD immunity and how does it affect isolators? How is it tested per IEC 61000-4-2?
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
What is ESD immunity and how does it affect isolators? How is it tested per IEC 61000-4-2?
*Please note that all definitions and references are based on the latest standard IEC 61000-4-2
Definition:
ESD is a miniature lightning bolt of charge that moves between two surfaces with different potentials. It can occur in four different ways: a charged body touches an IC, a charged IC touches a grounded surface, a charged machine touches an IC, or an electrostatic field can induce a voltage across a dielectric that is sufficient enough to break it down. The standard for ESD testing is defined by IEC 61000-4-2 which states the equipment, setup, procedure, and format of the test result.
Why is ESD immunity important in isolated systems?
During assembly, handling, or operation electrostatic discharges can occur and cause damage to a system. It’s important that the isolation barrier, and its communication bus, are able to withstand ESD to prevent data corruption, maintain system safety, and avoid system failure.
Test level
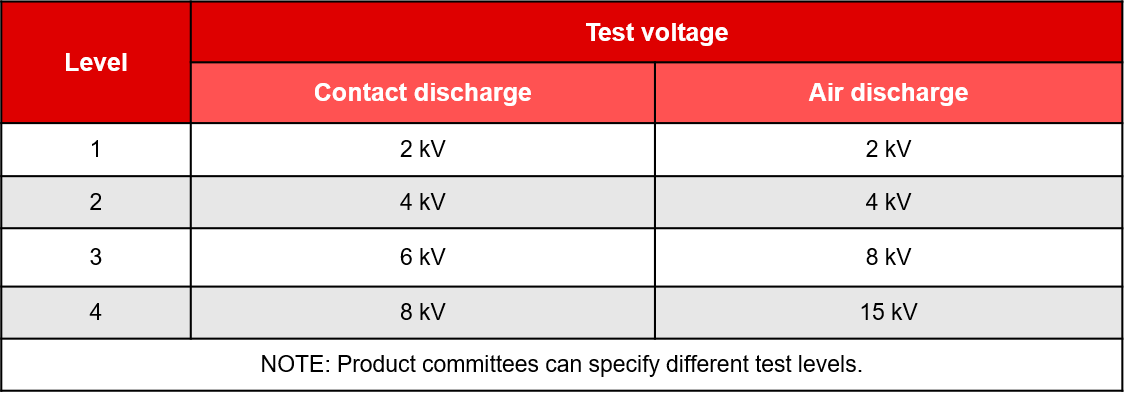
The ESD immunity test is conducted successively at levels 1-4 with the option of adding additional levels above, below, or in between the others. Level 1 represents the lowest required test with a contact discharge voltage of 2kV while level 4 represents the highest with a voltage of 8kV. Additionally, the test can be conducted in different mediums such as oil and air.
Test equipment
Simplified circuit of ESD generator

Rc – Charging resistor Cd – Impulse duration shaping resistors
Cs – Energy storage capacitor Rd – Impedance matching resistor
The following equipment is used in the test setup:
Test setup & procedure
Example of table-top test setup

The DUT is isolated from the RGP by a non-conductive table and its cables are isolated from the RGP by an insulating support. In the case of indirect discharges, a square VCP is situated between 0.1m – 0.001m from the side of the DUT and connected to the RGP through a VCP bleeder resistor cable.
For contact discharge, the tip of the ESD generator is placed in contact with a conductive pin on the DUT before the discharge switch is operated. In the case of air discharge, the ESD generator is triggered before contact between the tip and the DUT’s pin. The generator then approaches the DUT as fast as possible, without causing any mechanical damage, touching a conductive pin to ensure the possibility of a discharge. After each strike the generator tip is removed from contact with the DUT before retriggering for the next strike. At each test level, the specified number of strikes for each polarity are completed with a minimum of 1 second between strikes.
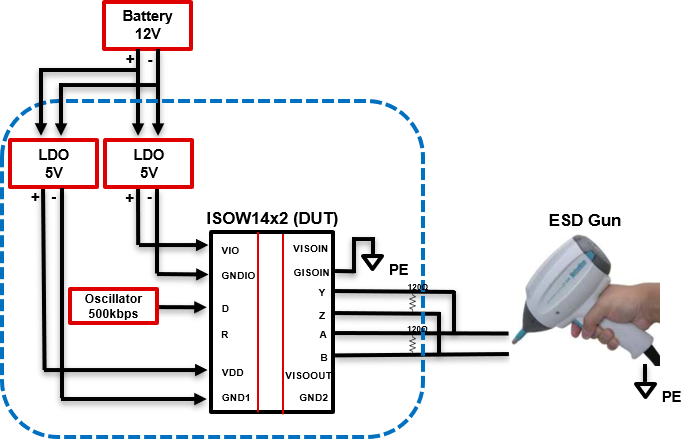
Example schematic of ISOxxxx under test:
Test Results
The results are evaluated by the performance level defined in test levels section above. They will be provided with a pass level, the medium it was tested in, the stress type, and the contact type:
Across Barrier:
ISOxxxx passes level 4 in oil using contact discharge
or…
Across Barrier:
ISOxxxx passes ±8kV in oil using contact discharge
Which means, ISOxxxx withstood ±8kV strikes without any loss of function or degradation of performance.