Hi Everyone.
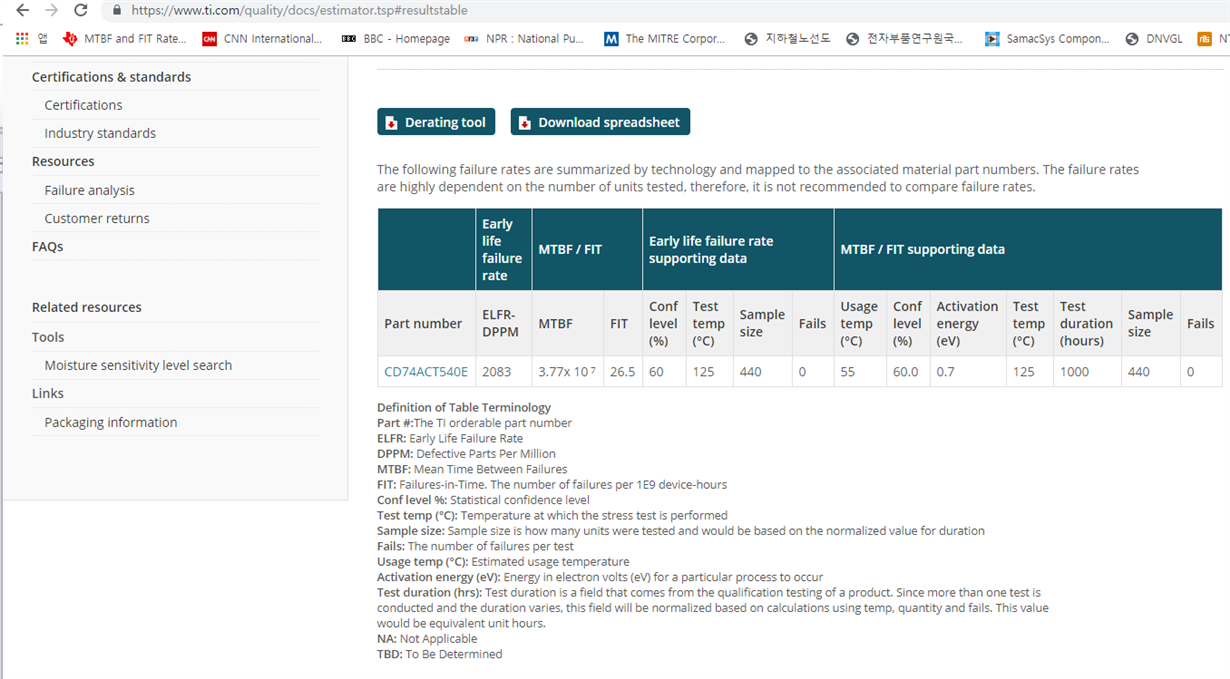
I have a question about the reliability data which are provided from the TI as the attached image below.
On the table, the confidence level is 60% and I want to convert to 90% or 95%.
Can anybody tell me how can I convert confidence level to get the corresponding MTBF or FIT values.
Thanks
Sean