Hi Team,
Customer has following question need your help:
1. When the motor is running in the state of a given desired high torque, if the given desired torque value is suddenly reduced to 0, the motor will suddenly increase its speed and then slowly stop. Why does the motor speed suddenly increase when the current is expected to decrease? Is it related to field weakening?
The following are some data waveform diagrams of test samples:
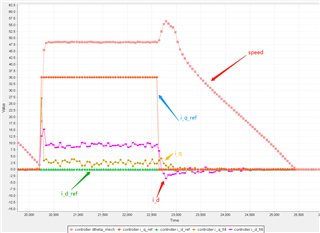
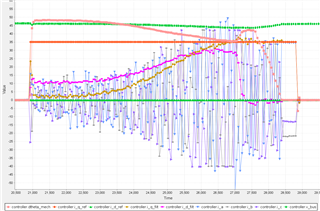
(The above figure is the current sampling and speed sampling curve in the torque loop test. It can be seen that when the expected value of the q-axis current suddenly drops to 0, the speed will rise for a period of time)
2. In the above-mentioned motor debugging environment, the MOS tube drive current setting value of the chip IDRIVE is changed through SPI, from 1000mA/2000mA to 60mA/120mA (the latter is closer to the most suitable parameter value of the MOS tube) .
The phenomenon of speed increase will change, and the time for the speed spike will be significantly shorter. What caused this change?
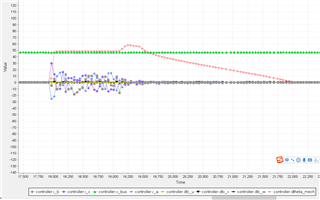
I_DRIVEP=1000mA,I_DRIVEN=2000mA
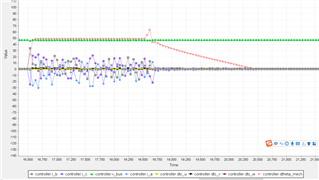
I_DRIVE=60mA,I_DRIVEN=120mA
(The pink curves in the above two figures are the actual speed of the motor feedback. It can be seen that the acceleration time in the figure below is obviously shorter, but the amplitude seems to be larger)
Thanks,
Annie