Tool/software:
How to reduce acoustic noise of MLCCs in TPS92205x and TPS92365x applications with PWM dimming?
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Tool/software:
How to reduce acoustic noise of MLCCs in TPS92205x and TPS92365x applications with PWM dimming?
TPS92205x and TPS92365x PWM dimming:
The TPS923650D1 and TPS923651D1 support PWM input signals with ultra-narrow pulse width down to 50-ns for direct PWM dimming. The PWM dimming starts when the DIM input pin is configured by a PWM input signal. When the PWM input signal at the DIM pin turns from low to high, the internal NMOS FET starts switching and the inductor current rises to the determined value set by sense resistor. The LED current is then regulated at the determined value as long as the PWM input signal stays high. When the PWM input signal turns from high to low, the internal FET is turned off causing the inductor current falling to zero. The internal FET maintains off and the LED current stays zero as long as the PWM input signal stays low.
Origin of audible noise:
Multi-layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCC) is widely used in electronic products due to its good performance, such as small size, low ESR, low cost, and so forth. However, when an AC voltage is applied to MLCC, it expands and shrinks due to the electrostrictive effect of the ferroelectric ceramic. As a result, the printed circuit board (PCB) vibrates in the surface direction as shown below. The vibration of capacitor and board is only about 1 pm – 1 nm, when the vibration frequency reaches the audio frequency range (20 Hz – 20 kHz) of humans, a sound is perceived by the human ear.
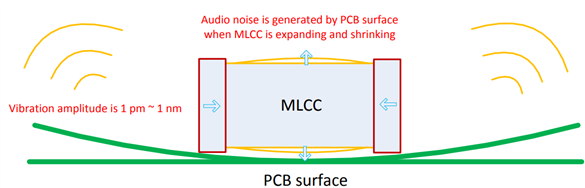
The inductor also has similar electrostrictive effect, but it is not common to observe the audio noise generated by the inductor with the advancement of inductor process, especially for the shielding inductor.
Solutions that can minimize or reduce noise to acceptable levels: