Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TPS563219A
Hi Sir,
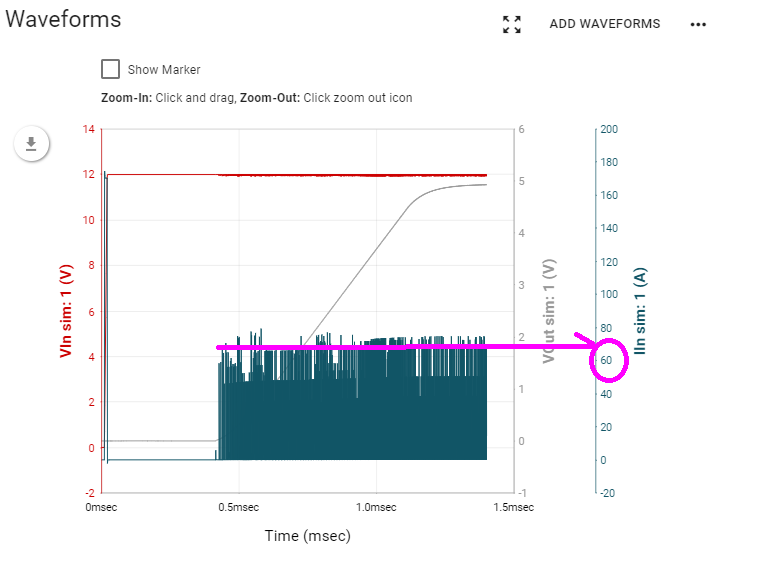
Is it possible to estimate or calculate the input inrush current from the circuits of TPS53219A and output load?
After trying to simulate the startup on WEBENCH, just found the waveform of input inrush current is weird and up to 60~80A.
Is this the same in practical application?
Thanks
Sincerely,
Edward