Tool/software:
Hello Everyone,
I am working on a project that involves TLV320aic3204 codec. I am confusing below given two: Can anyone Clarify ?
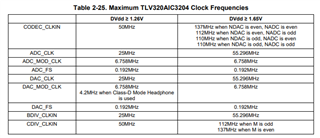
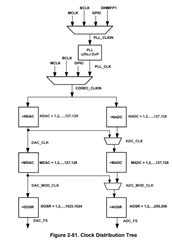
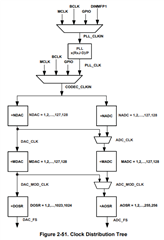
1. The required internal clock of the TLV320AIC3204 can be derived from multiple sources, including the
MCLK pin, the BCLK pin, the GPIO pin or the output of the internal PLL, where the input to the PLL again
can be derived from the MCLK pin, the BCLK or GPIO pins. Although using the PLL ensures the
availability of a suitable clock signal, it is not recommended for the lowest power settings. The PLL is
highly programmable and can accept available input clocks in the range of 512kHz to 50MHz.
2.The PLL input supports clocks varying from 512kHz to 20MHz and is register programmable to enable
generation of required sampling rates with fine resolution. The PLL can be turned on by writing to Page 0,
Register 5, D(7).
Can Anyone clarify above two red marked statements. I read that statements in the given aplication reference manual: www.tij.co.jp/.../slaa557.pdf
Thank you in advance