Tool/software:
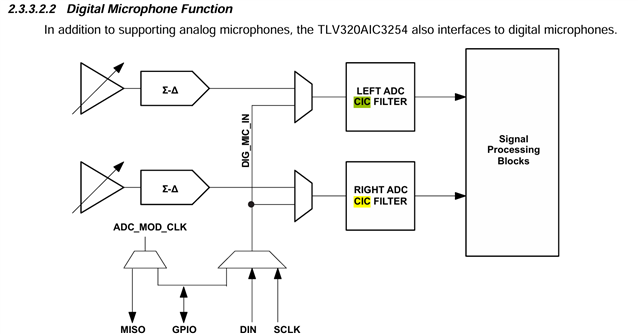
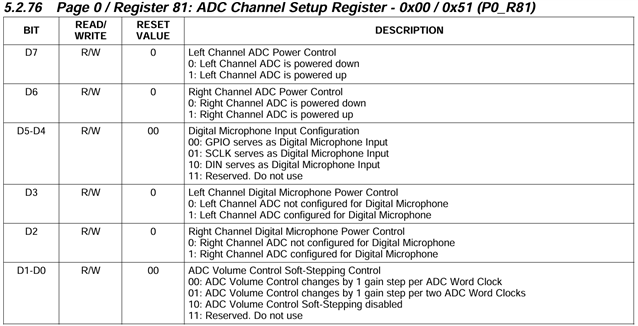
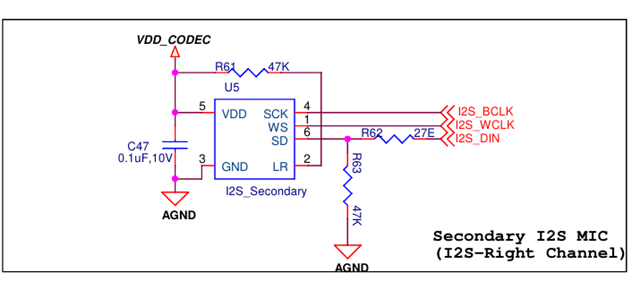
I am working with the TLV320AIC3254 codec in my project. I have two analog microphones and two digital microphones connected to the codec. I want to be able to use either the analog or digital microphones for signal processing.
My requirement is to perform different noise cancellation techniques, such as:
-
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC)
-
Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC)
-
Beamforming
-
Adaptive Filters
I have a few questions regarding the codec:
-
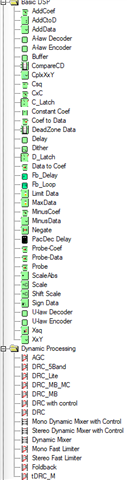
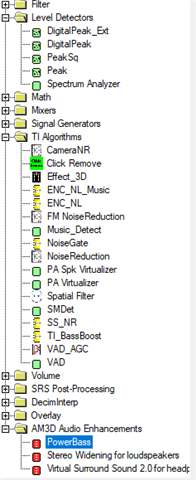
What is the purpose of the processing block and the miniDSP in the TLV320AIC3254? Are these two designed to do the same work, or do they serve different purposes? If different, could you explain what type of operations can be implemented in the processing block versus the miniDSP?
-
What is the recommended way to use the miniDSP versus the processing blocks in the TLV320AIC3254 in the Pure Path Studio? In which cases should I rely on the built-in processing blocks, and in which cases should I program the miniDSP using PurePath Studio?
-
From the TI support forums, I found the note:
-
“It cannot keep up with modern expectations of AEC and ANC. We strongly discourage designers from using the DSP in the codec to host the algorithm and instead host the algorithm on a separate DSP or SoC.”
Based on this, I would like to confirm: Is it correct that advanced algorithms like ANC and AEC cannot be fully supported in the codec’s miniDSP, and are better implemented on an external DSP/SoC?
-
-
I also found a note saying:
-
“Adaptive filtering function will not be able to provide noise cancellation. Noise cancellation requires inverting the noise and using it to cancel the noise, rather than just using biquad filtering to filter it out.”
Could you please clarify this statement in the context of the miniDSP? Does it mean the adaptive filter blocks in the codec are not sufficient for real ANC implementations.
-
- could you please suggest which noise cancellation techniques are practically possible to implement on the TLV320AIC3254 codec itself?
-