Dear TI Community,
I'm very sorry for the really basic question.
Please teach me about ADS9120.
I designed circuit as shown on the next-figure.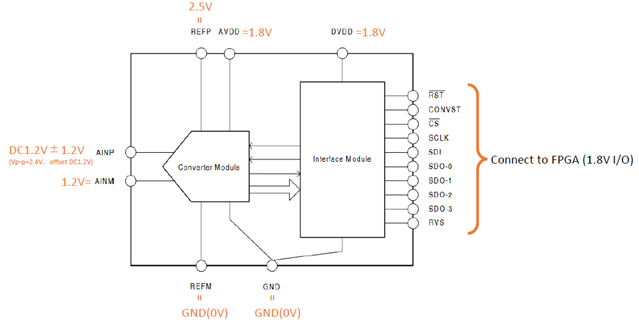
I think as follows:
The ADC full scale is defined by VREFP / M.
-> In this case, the range from 0 to 2.5V.
ADC CODE 0000 is specified by AINM voltage.
-> In this case, 1.2V.
Is this understanding correct?
In this case, I think that the data can be read as shown in the figure below.
Is this understanding correct?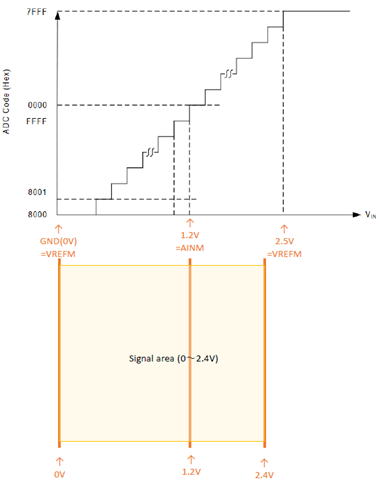
In the case of the configuration, I assume that there is a non-linearity region near 0V.
Is linearity around 0V guaranteed for this device?
If not guaranteed, how much voltage should be considered for non-linearity near 0V?
Thank you for your cooperation,
Tanigawa

