Hi team,
Using the ADS1294 as a dual-channel electromyography acquisition, to increase the input impedance, an instrumentation amplifier, AD8222, was added to the front end, 100 times amplified and single ended to the ADS1294. The detailed circuit diagram is as follows:
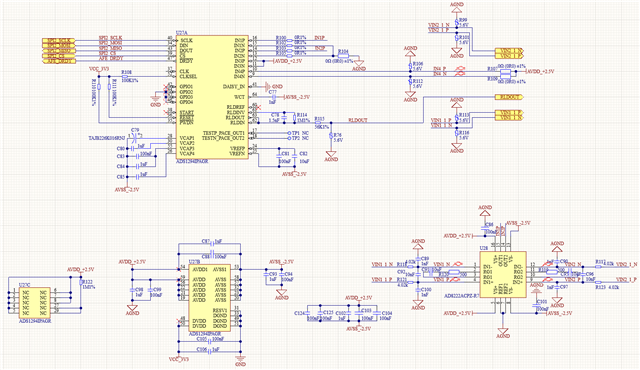
Measurement result: In indoor office environments, line frequency interference is severe and the signal cannot be measured without the RLD electrode connected. The interference improves a lot with the RLD electrode connected, but it still exists, much like the one using the myoelectric differential-mode signal. However, when measuring outdoors, it basically meets the customer's requirements.
The customer is assuming that the RLD amplifier gain setting is not sufficient to completely cancel line frequency interference. The test circuit is battery powered and the MCU captures the ADS conversion data and sends it to the PC via the serial-to-USB cable. Formal products also include those sent to a PC via a wifi module, which means that there is no cable connection.
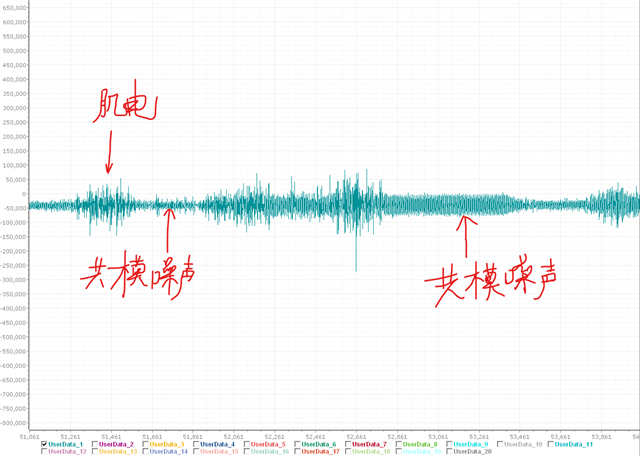
(The Chinese text in the figure above represents the electromyography, the common-mode noise, the common-mode noise)
Could you help check this case? Thanks.
Best Regards,
Cherry

