Other Parts Discussed in Thread: MSP432E401Y, ADS131M08
Tool/software:
Hi,
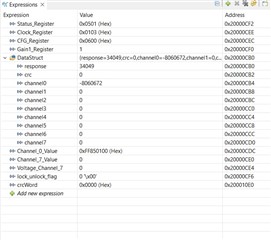
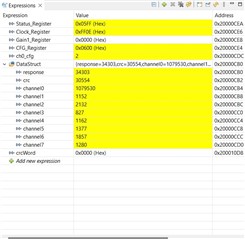
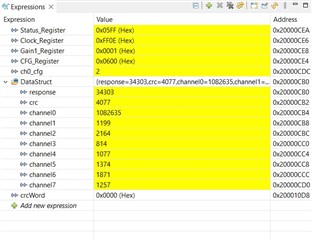
I am able to read, write and re-write any of the settings registers. So the SPI works (I have connected my EVM to a MSP432E401Y Launchpad). I am trying to apply a known signal from the function generator,
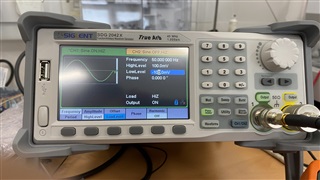
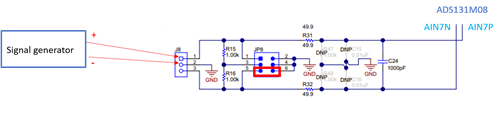
The +ve goes to the + side of J8 (I am using channel 7) and the gnd of the function generator is tied to the EVM and launchpad gnds and provided to the - of the J8. The JP8 jumper is in the default position (middle). Please see the attached image.

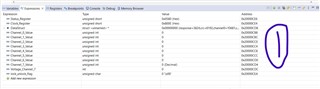
I have enabled channel7, and I can see it in the clock register (attached image).

I don't get the correct data entry. Whatever I change the input, the value seems to be fixed. Is my jumper and connections settings correct? I even switched my jumper to JP8 [5-6], but I don't seem to read the data correctly.
Thanks
Ram.