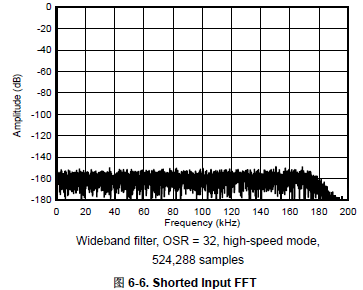
Tool/software:
I want to know how the 6.11 figure in datasheet was tested.
What’s the meaning of "Short input FFT"
What is the output(y axis) in the graph ?
From which terminal(pin) this amount is measured ?
What does this data represent about ADC performance? It doesn't seem like data like ENOB is intuitive and generic ?
I would like to have an answer from the relevant engineer . THANKS!