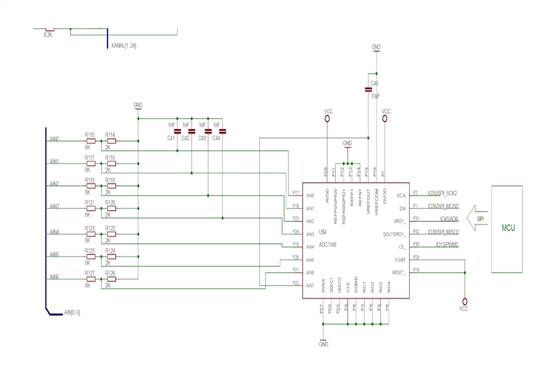
I have read the datasheet of "ADS1148" and there are 7 Single-Ended Inputs on the "ADS1148", but there is no application circuit example for the Single-Ended Inputs on the datasheet.
There are too many pins on "ADS1148" and I am not sure how to use them.
I want to measure 7 analogsignals and the area of analogsignal is 0 to 10V.
Can you give me a application circuit for 7 Single-Ended Inputs?
I look forward to your answer.