Other Parts Discussed in Thread: DS160PR810, LMH0340
IBIS stands for Input/Output Buffering Information Specifications while AMI stands for Algorithm modeling Interface.
In short, IBIS is used to describe analog behavior of the input or output structure of the buffer or device while IBIS-AMI also
discusses high speed signal path behavior. Here are some details about each model:
IBIS-AMI:
1). Typically comes with DLL and s-parameter files to enable a simulation environment where the user can speficy ASIC TX, ASIC RX,
and transmission media. Using this environment the user can do signal integrity analyses.
2). S-parameter files can be used to check/study s-parameter behavior across signal frequency of interest.
3). ASIC TX, RX, and device under test jitter dependent behavior signal integrity can be studied and analyzed.
4). Allows ASIC and DUT study of equalization on both transmit and receive sides.
5). Mainly used for giga bit/bits per second high speed signal modeling
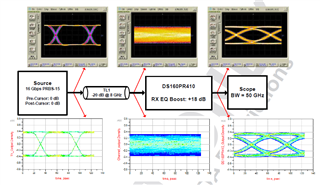
6). Figure below shows IBIS-AMI result using BERT, TL1 s-parameter, DS160PR810 EQ boost model, and ouput eye diagram using real time scope and comparing with IBIS-AMI result:
IBIS:
1). Typically it is a single file that allows study of analog buffer on TX and RX sides
2). ESD structure, output/input buffer, and device package lumped behavior is modeled
3). Used for low speed less than giga bits per second analog buffer behavior
4). Mainly used for I vs. V similar to a curve tracer and V vs time
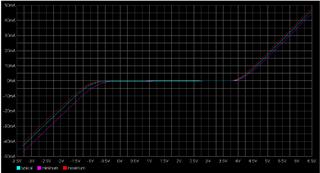
5). Figure below shows I vs V of LVDS input of the LMH0340:
Regards, Nasser

