Tool/software:
Hello,
We have few concerns on the ISOW1432 part design.Can someone clarify below questions.
1. To change to half duplex mode we need to short Driver outputs Y and Z are shorted to A and B respectively and the split termination is provided between A and B but in EVB board the Split termination is provided a between Y and Z. Please clarify which one to follow.
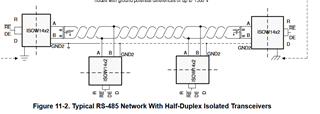

2. How to change to RS422 transceiver mode.
3. Does ESD diodes required for this isolated transceiver module.
4. GND2 reference is required for differential pair if we route that in top and bottom layers.
5 Common mode choke is necessary , if so suggest part numbers (not available in EVB)
6. Suggestions for trace width of A/B/Y/Z.
7. Minimum stub length in PCB side.



