FAQ: Logic and Voltage Translation > Output Parameters >> Current FAQ
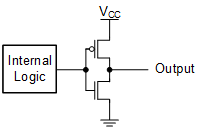
Push-Pull Output
A push-pull output can source current in the high state or sink current in the low state. In modern CMOS devices, the most common configuration for a push-pull output is shown here:
|
Output State |
Positive Driver ( pFET ) |
Negative Driver ( nFET ) |
| HIGH | ON | OFF |
| LOW | OFF | ON |
When the output is in the high state:
The p-channel MOSFET is on and sources current from VCC to the output.
The n-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow to GND.
When the output is in the low state:
The p-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow from VCC.
The n-channel MOSFET is on and sinks current from the output to GND.
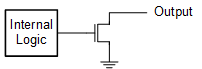
Open-Drain Output
An open-drain output can only sink current in the low state. In modern CMOS devices, the most common configuration for an open-drain output is shown here:
|
Output State |
Negative Driver ( nFET ) |
| Hi-Z | OFF |
| LOW | ON |
When the output is in the high-impedance state, the n-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow any current to flow.
When the output is in the low state, the n-channel MOSFET is on and sinks current from the output to GND.
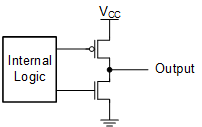
3-State Output
A 3-state output can be in one of three states: driving high, driving low, or not driving (high impedance). The most common configuration for a 3-state output is shown here:
|
Output State |
Positive Driver ( pFET ) |
Negative Driver ( nFET ) |
| HIGH | ON | OFF |
| LOW | OFF | ON |
| Hi-Z | OFF | OFF |
When the output is in the high state:
The p-channel MOSFET is on and sources current from VCC to the output.
The n-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow to GND.
When the output is in the low state:
The p-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow from VCC.
The n-channel MOSFET is on and sinks current from the output to GND.
When the output is in the high-impedance state:
The p-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow from VCC.
The n-channel MOSFET is off and does not allow current to flow to GND.