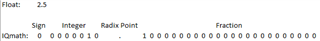Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE
Hi All,
What is the difference between below 2 functions in IQ math lib.
1.) _IQ(2.0);
2.) _IQ2toIQ(2.0);
Also, Please elaborate when to use function 1 and function 2 with an individual example.
Also, please let me know that "Q24" means 24 Integer bit or fraction resolution in Q24 format?
Thanks & Regards,