Other Parts Discussed in Thread: LAUNCHXL-F280049C, TMS320F280039C
Hi C2000 experts,
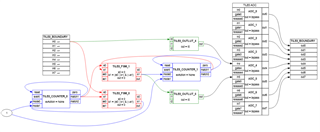
I want to synchronize ePWM modules on multiple devices via FSI in star topology. For this I played around with your example project "fsi_daisy_epwmsync_lead" on the LAUNCHXL-F280049C. I have a few questions about this.
For the sake of simplicity, I used the FSI loopback mode on a single F280049C controller. I configured the PWM slightly different and skipped the handshake initialization. I start a ping frame manually inside the debug session. If needed I can paste the code, but it should have no relation to my questions.
Here you can see a measurement:
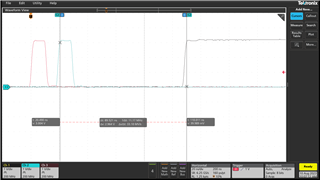
Ch1 (black): ePWM1A (set when TBCTR = 0, cleared when TBCTR = PRD)
Ch2 (blue): EPWMSYNCIN (EPWMSYNCIN signal with delay from CLB, according to the example)
Ch3 (red): FSIRXA PING Packet Received / CLB_GLOBAL_IN_MUX_FSIRXA_PING_PACKET_RCVD (EPWMSYNCIN signal without delay, according to the example)
SYSCLK = EPWMCLK = 100 MHz
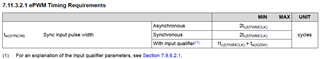
The pulse width of the "FSIRXA PING Packet Received" signal is only about one SYSCLK period. The CLB logic generates a delayed singal which is used as EXTSYNCIN1 in the ePWM. However, this signal is also only one SYSCLK period wide. In the data sheet SPRS945G of the controller, however, in section 7.11.3.2.1 a minimum pulse duration of two EPWMCLK cycles is required (asychronous). Since EPWMCLK is equal to SYSCLK, this time is violated. I have extended the pulse length up to 5 SYSCLK cycles by changing the clb configuration. But I found out that a longer pulse does not cause any change.
1) Is the synchronization of the example operated outside the specification, or is the value in the data sheet incorrect?
The cursors shows the latency between EPWMSYNCIN impulse and synchronization event. The delay is about 90 ns, which corresponds to 9 EPWMCLK cycles.
2) Is this delay specified anywhere in the TRM or in the data sheet?
3) Is this delay the same for all devices with type 4 ePWM units?
I found this in chapter 18.4.3.3. of the TRM SPRUI33F:

I assume that with internal module already an ePWM is meant and the delay of a chain, e.g. EXTSYNCIN1-> ePWM1 -> ePWM2 is described. Is this correct?
4) Is there any specification about the pulse length of the FSIRX pulses e.g. for FSIRXA PING Packet Received? I have not found anything in the TRM nor in the datasheet.
By measurements I found out that these pulse widths correspond to one SYSCLK period with type 0 FSI. With a FSI type 2, however, I could measure eight SYSCLK periods.
Thank you very much in advance.
Regards, Stefan