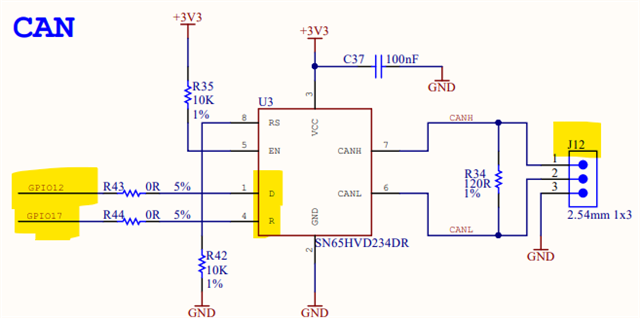
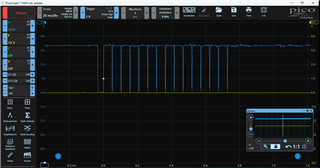
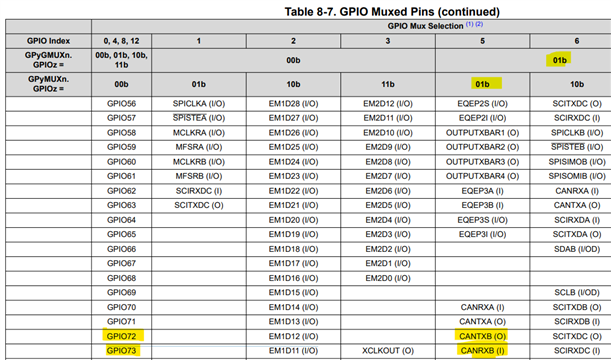
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE
Tool/software:
Hi
whenever i try to Disable these two registers
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.bit.Test = 1;
CanaRegs.CAN_TEST.bit.EXL = 1;
data does not come into a CANTX pin.
please suggest me what's going wrong in this code
//###########################################################################
//
// FILE: can_loopback_bitfields.c
//
// TITLE: Example to demonstrate basic CAN setup and use.
//
//! \addtogroup cpu01_example_list
//! <h1>CAN External Loopback Using Bitfields (can_loopback_bitfields)</h1>
//!
//! IMPORTANT: CAN Bitfield headers require compiler v16.6.0.STS and newer!
//!
//! This example, using bitfield headers, shows the basic setup of CAN in
//! order to transmit and receive messages on the CAN bus. The CAN
//! peripheral is configured to transmit messages with a specific CAN ID.
//! A message is then transmitted once per second, using a simple delay
//! loop for timing. The message that is sent is a 4 byte message that
//! contains an incrementing pattern.
//!
//! This example sets up the CAN controller in External Loopback test mode.
//! Data transmitted is visible on the CAN0TX pin and can be received with
//! an appropriate mailbox configuration.
//!
//
//###########################################################################
//
// $Release Date: $
// $Copyright:
// Copyright (C) 2013-2023 Texas Instruments Incorporated - http://www.ti.com/
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
// are met:
//
// Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
// documentation and/or other materials provided with the
// distribution.
//
// Neither the name of Texas Instruments Incorporated nor the names of
// its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
// from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
// $
//###########################################################################
//
// Included Files
//
#include "F28x_Project.h"
//
// Defines
//
#define CAN_MSG_ID 0x111 // This example only supports standard ID
#define CAN_TX_MSG_OBJ 1
#define CAN_RX_MSG_OBJ 2
#define CAN_MAX_BIT_DIVISOR (13) // The maximum CAN bit timing divisor
#define CAN_MIN_BIT_DIVISOR (5) // The minimum CAN bit timing divisor
#define CAN_MAX_PRE_DIVISOR (1024) // The maximum CAN pre-divisor
#define CAN_MIN_PRE_DIVISOR (1) // The minimum CAN pre-divisor
#define CAN_BTR_BRP_M (0x3F)
#define CAN_BTR_BRPE_M (0xF0000)
#define CAN_MSG_ID_SHIFT 18U
//
// Globals
//
unsigned char ucTXMsgData[4] = {0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4}; // TX Data
unsigned char ucRXMsgData[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0}; // RX Data
uint32_t messageSize = sizeof(ucTXMsgData); // Message Size (DLC)
volatile unsigned long msgCount = 0; // A counter that keeps track of the
// number of times the transmit was
// successful.
volatile unsigned long errFlag = 0; // A flag to indicate that some
// transmission error occurred.
static const uint16_t canBitValues[] =
{
0x1100, // TSEG2 2, TSEG1 2, SJW 1, Divide 5
0x1200, // TSEG2 2, TSEG1 3, SJW 1, Divide 6
0x2240, // TSEG2 3, TSEG1 3, SJW 2, Divide 7
0x2340, // TSEG2 3, TSEG1 4, SJW 2, Divide 8
0x3340, // TSEG2 4, TSEG1 4, SJW 2, Divide 9
0x3440, // TSEG2 4, TSEG1 5, SJW 2, Divide 10
0x3540, // TSEG2 4, TSEG1 6, SJW 2, Divide 11
0x3640, // TSEG2 4, TSEG1 7, SJW 2, Divide 12
0x3740 // TSEG2 4, TSEG1 8, SJW 2, Divide 13
};
typedef enum
{
//! Transmit message object.
MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TRANSMIT,
//! Receive message object.
MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RECEIVE
}
msgObjType;
//
// Function Prototypes
//
uint32_t setCANBitRate(uint32_t sourceClock, uint32_t bitRate);
void setupMessageObject(uint32_t objID, uint32_t msgID, msgObjType msgType);
void sendCANMessage(uint32_t objID);
bool getCANMessage(uint32_t objID);
void CAN_A_B_GPIO();
//
// Main
//
int
main(void)
{
//
// Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the F2837xD_SysCtrl.c file.
//
InitSysCtrl();
//
// Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the F2837xD_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to its default state.
//
// InitGpio();
// GPIO_SetupPinMux(70, GPIO_MUX_CPU1, 5); //GPIO39 - CANRXA
// GPIO_SetupPinMux(71, GPIO_MUX_CPU1, 5); //GPIO38 - CANTXA
// GPIO_SetupPinOptions(70, GPIO_INPUT, GPIO_ASYNC);
// GPIO_SetupPinOptions(71, GPIO_OUTPUT, GPIO_PUSHPULL);
CAN_A_B_GPIO();
//
// Initialize the CAN-A controller
//
InitCAN();
//
// Setup CAN to be clocked off the SYSCLKOUT
//
ClkCfgRegs.CLKSRCCTL2.bit.CANABCLKSEL = 0;
//
// Set up the bit rate for the CAN bus. This function sets up the CAN
// bus timing for a nominal configuration.
// In this example, the CAN bus is set to 500 kbps.
//
// Consult the TRM for more information about
// CAN peripheral clocking.
//
uint32_t status = setCANBitRate(200000000, 5000000);
//
// If values requested are too small or too large, catch error
//
if(status == 0)
{
errFlag++;
ESTOP0; // Stop here and handle error
}
//
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
//
DINT;
//
// Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the F2837xD_PieCtrl.c file.
//
InitPieCtrl();
//
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
//
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in F2837xD_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in F2837xD_PieVect.c.
//
InitPieVectTable();
//
// Enable the CAN for operation.
//
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.bit.Init = 0;
//
// Enable test mode and select external loopback
//
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.bit.Test = 1;
CanaRegs.CAN_TEST.bit.EXL = 1;
//
// Initialize the message object that will be used for sending CAN
// messages.
//
setupMessageObject(CAN_TX_MSG_OBJ, CAN_MSG_ID, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TRANSMIT);
//
// Initialize the message object that will be used for receiving CAN
// messages.
//
setupMessageObject(CAN_RX_MSG_OBJ, CAN_MSG_ID, MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RECEIVE);
//
// Enter loop to send messages. A new message will be sent once per
// second. The 4 bytes of message content will be treated as an unsigned
// long and incremented by one each time.
//
for(;;)
{
//
// Send the CAN message using object number 1 (not the same thing as
// CAN ID, which is also 1 in this example). This function will cause
// the message to be transmitted right away.
//
sendCANMessage(CAN_TX_MSG_OBJ);
//
// Now wait 1 second before continuing
//
DELAY_US(1000*1000);
//
// Get the receive message
//
getCANMessage(CAN_RX_MSG_OBJ);
//
// Ensure the received data matches the transmitted data
//
if((ucTXMsgData[0] != ucRXMsgData[0]) ||
(ucTXMsgData[1] != ucRXMsgData[1]) ||
(ucTXMsgData[2] != ucRXMsgData[2]) ||
(ucTXMsgData[3] != ucRXMsgData[3]))
{
errFlag++;
//asm(" ESTOP0");
}
else
{
//
// Increment successful message count
//
msgCount++;
}
//
// Increment the value in the transmitted message data.
//
ucTXMsgData[0] += 0x1;
ucTXMsgData[1] += 0x1;
ucTXMsgData[2] += 0x1;
ucTXMsgData[3] += 0x1;
//
// Reset data if exceeds a byte
//
if(ucTXMsgData[0] > 0xFF)
{
ucTXMsgData[0] = 0;
}
if(ucTXMsgData[1] > 0xFF)
{
ucTXMsgData[1] = 0;
}
if(ucTXMsgData[2] > 0xFF)
{
ucTXMsgData[2] = 0;
}
if(ucTXMsgData[3] > 0xFF)
{
ucTXMsgData[3] = 0;
}
}
}
//
// setCANBitRate - Set the CAN bit rate based on device clock (Hz)
// and desired bit rate (Hz)
//
uint32_t setCANBitRate(uint32_t sourceClock, uint32_t bitRate)
{
uint32_t desiredRatio;
uint32_t canBits;
uint32_t preDivide;
uint32_t regValue;
uint16_t canControlValue;
//
// Calculate the desired clock rate.
//
desiredRatio = sourceClock / bitRate;
//
// Make sure that the Desired Ratio is not too large. This enforces the
// requirement that the bit rate is larger than requested.
//
if((sourceClock / desiredRatio) > bitRate)
{
desiredRatio += 1;
}
//
// Check all possible values to find a matching value.
//
while(desiredRatio <= CAN_MAX_PRE_DIVISOR * CAN_MAX_BIT_DIVISOR)
{
//
// Loop through all possible CAN bit divisors.
//
for(canBits = CAN_MAX_BIT_DIVISOR;
canBits >= CAN_MIN_BIT_DIVISOR;
canBits--)
{
//
// For a given CAN bit divisor save the pre divisor.
//
preDivide = desiredRatio / canBits;
//
// If the calculated divisors match the desired clock ratio then
// return these bit rate and set the CAN bit timing.
//
if((preDivide * canBits) == desiredRatio)
{
//
// Start building the bit timing value by adding the bit timing
// in time quanta.
//
regValue = canBitValues[canBits - CAN_MIN_BIT_DIVISOR];
//
// To set the bit timing register, the controller must be
// placed
// in init mode (if not already), and also configuration change
// bit enabled. The state of the register should be saved
// so it can be restored.
//
canControlValue = CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.all;
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.bit.Init = 1;
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.bit.CCE = 1;
//
// Now add in the pre-scalar on the bit rate.
//
regValue |= ((preDivide - 1) & CAN_BTR_BRP_M) |
(((preDivide - 1) << 10) & CAN_BTR_BRPE_M);
//
// Set the clock bits in the and the bits of the
// pre-scalar.
//
CanaRegs.CAN_BTR.all = regValue;
//
// Restore the saved CAN Control register.
//
CanaRegs.CAN_CTL.all = canControlValue;
//
// Return the computed bit rate.
//
return(sourceClock / ( preDivide * canBits));
}
}
//
// Move the divisor up one and look again. Only in rare cases are
// more than 2 loops required to find the value.
//
desiredRatio++;
}
return 0;
}
//
// setupMessageObject - Setup message object as Transmit or Receive
//
void setupMessageObject(uint32_t objID, uint32_t msgID, msgObjType msgType)
{
//
// Use Shadow variable for IF1CMD. IF1CMD should be written to in
// single 32-bit write.
//
union CAN_IF1CMD_REG CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW;
//
// Wait for busy bit to clear.
//
while(CanaRegs.CAN_IF1CMD.bit.Busy)
{
}
//
// Clear and Write out the registers to program the message object.
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.all = 0;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1MSK.all = 0;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1ARB.all = 0;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1MCTL.all = 0;
//
// Set the Control, Mask, and Arb bit so that they get transferred to the
// Message object.
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.Control = 1;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.Arb = 1;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.Mask = 1;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.DIR = 1;
//
// Set direction to transmit
//
if(msgType == MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TRANSMIT)
{
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1ARB.bit.Dir = 1;
}
//
// Set Message ID (this example assumes 11 bit ID mask)
//
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1ARB.bit.ID = (msgID << CAN_MSG_ID_SHIFT);
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1ARB.bit.MsgVal = 1;
//
// Set the data length since this is set for all transfers. This is
// also a single transfer and not a FIFO transfer so set EOB bit.
//
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1MCTL.bit.DLC = messageSize;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1MCTL.bit.EoB = 1;
//
// Transfer data to message object RAM
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.MSG_NUM = objID;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1CMD.all = CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.all;
}
//
// sendCANMessage - Transmit data from the specified message object
//
void sendCANMessage(uint32_t objID)
{
//
// Use Shadow variable for IF1CMD. IF1CMD should be written to in
// single 32-bit write.
//
union CAN_IF1CMD_REG CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW;
//
// Wait for busy bit to clear.
//
while(CanaRegs.CAN_IF1CMD.bit.Busy)
{
}
//
// Write data to transfer into DATA-A and DATA-B interface registers
//
uint16_t index;
for(index = 0; index < messageSize; index++)
{
switch(index)
{
case 0:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATA.bit.Data_0 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 1:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATA.bit.Data_1 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 2:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATA.bit.Data_2 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 3:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATA.bit.Data_3 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 4:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATB.bit.Data_4 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 5:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATB.bit.Data_5 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 6:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATB.bit.Data_6 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
case 7:
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1DATB.bit.Data_7 = ucTXMsgData[index];
break;
}
}
//
// Set Direction to write and set DATA-A/DATA-B to be transfered to
// message object
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.all = 0;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.DIR = 1;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.DATA_A = 1;
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.DATA_B = 1;
//
// Set Tx Request Bit
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.TXRQST = 1;
//
// Transfer the message object to the message object specified by
// objID.
//
CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.bit.MSG_NUM = objID;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF1CMD.all = CAN_IF1CMD_SHADOW.all;
}
//
// getCANMessage - Check the message object for new data.
// If new data, data written into array and return true.
// If no new data, return false.
//
bool getCANMessage(uint32_t objID)
{
bool status;
//
// Use Shadow variable for IF2CMD. IF2CMD should be written to in
// single 32-bit write.
//
union CAN_IF2CMD_REG CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW;
//
// Set the Message Data A, Data B, and control values to be read
// on request for data from the message object.
//
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.all = 0;
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.Control = 1;
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.DATA_A = 1;
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.DATA_B = 1;
//
// Transfer the message object to the message object IF register.
//
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.MSG_NUM = objID;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF2CMD.all = CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.all;
//
// Wait for busy bit to clear.
//
while(CanaRegs.CAN_IF2CMD.bit.Busy)
{
}
//
// See if there is new data available.
//
if(CanaRegs.CAN_IF2MCTL.bit.NewDat == 1)
{
//
// Read out the data from the CAN registers.
//
uint16_t index;
for(index = 0; index < messageSize; index++)
{
switch(index)
{
case 0:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATA.bit.Data_0;
break;
case 1:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATA.bit.Data_1;
break;
case 2:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATA.bit.Data_2;
break;
case 3:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATA.bit.Data_3;
break;
case 4:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATB.bit.Data_4;
break;
case 5:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATB.bit.Data_5;
break;
case 6:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATB.bit.Data_6;
break;
case 7:
ucRXMsgData[index] = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2DATB.bit.Data_7;
break;
}
}
//
// Populate Shadow Variable
//
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.all = CanaRegs.CAN_IF2CMD.all;
//
// Clear New Data Flag
//
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.TxRqst = 1;
//
// Transfer the message object to the message object IF register.
//
CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.bit.MSG_NUM = objID;
CanaRegs.CAN_IF2CMD.all = CAN_IF2CMD_SHADOW.all;
status = true;
}
else
{
status = false;
}
return(status);
}
void CAN_A_B_GPIO(){
EALLOW;
/*****************CAN_A (CANRXA (I)) *****************/
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCGMUX1.bit.GPIO70 = 0x01;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCMUX1.bit.GPIO70 = 0x01;
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCDIR.bit.GPIO70 = 0x00; //Configure as Output, 0 for Input and 1 for Output
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCINV.bit.GPIO70 = 0x00; //0 for non inverted Output, 1 for inverted Output
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCPUD.bit.GPIO70 = 0x00; //0 for Enable Pull up, 1 for Disable Pull up
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCQSEL1.bit.GPIO70 = 0x03;
/*****************CAN_A (CANTXA (O)) *****************/
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCGMUX1.bit.GPIO71 = 0x01;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCMUX1.bit.GPIO71 = 0x01;
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCDIR.bit.GPIO71 = 0x01; //Configure as Output, 0 for Input and 1 for Output
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCINV.bit.GPIO71 = 0x00; //0 for non inverted Output, 1 for inverted Output
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCPUD.bit.GPIO71 = 0x00; //0 for Enable Pull up, 1 for Disable Pull up
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCQSEL1.bit.GPIO71 = 0x03;
/*****************CAN_B (CANTXB (O)) *****************/
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCGMUX1.bit.GPIO72 = 0x01;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCMUX1.bit.GPIO72 = 0x01;
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCDIR.bit.GPIO72 = 0x01; //Configure as Output, 0 for Input and 1 for Output
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCINV.bit.GPIO72 = 0x00; //0 for non inverted Output, 1 for inverted Output
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCPUD.bit.GPIO72 = 0x00; //0 for Enable Pull up, 1 for Disable Pull up
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCQSEL1.bit.GPIO72 = 0x03;
/*****************CAN_B (CANRXB (I)) *****************/
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCGMUX1.bit.GPIO73 = 0x01;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCMUX1.bit.GPIO73 = 0x01;
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCDIR.bit.GPIO73 = 0x00; //Configure as Output, 0 for Input and 1 for Output
// GpioCtrlRegs.GPCINV.bit.GPIO73 = 0x00; //0 for non inverted Output, 1 for inverted Output
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCPUD.bit.GPIO73 = 0x00; //0 for Enable Pull up, 1 for Disable Pull up
GpioCtrlRegs.GPCQSEL1.bit.GPIO73 = 0x03;
EDIS;
}
//
// End of file
//