Tool/software:
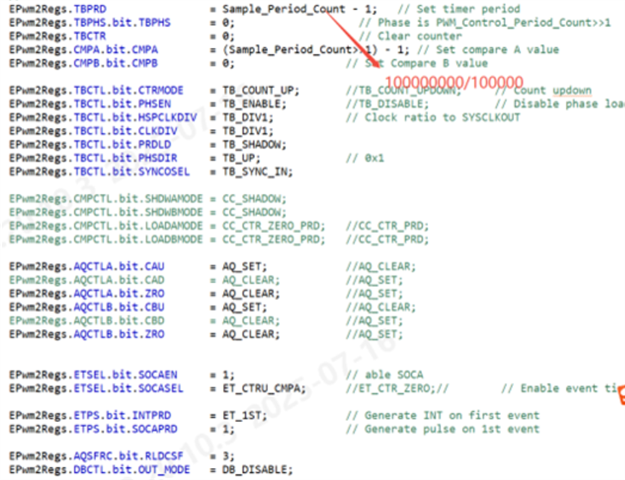
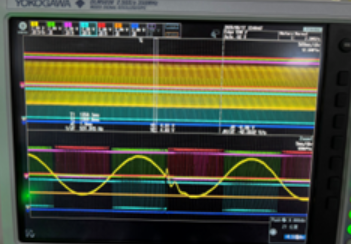
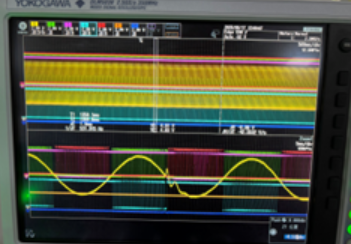
In the NPC three-level topology, when discharging and the positive half-cycle is cut from the negative half-cycle, one tube shows an abnormal pulse width, with a pulse width duration of approximately 400 microseconds. Before the positive half-cycle of discharge switches to the negative half-cycle, the current direction is outward. When tube 1 reaches its full duty cycle, the current rises, and the slope of the current increase is very large. The three-phase drives of A, B and C respectively use EPWM1, EPWM3 and EPWM5, and the three configurations are the same. Sampling is triggered by EPWM2. The configuration methods of EPWM1 and EPWM2 are shown in the figure. control.cla is triggered by EPWM11 with an interrupt frequency of 10k. The synchronization mode of EPWM1,3, and 5 is external input signal synchronization, and the synchronization signal is triggered once every 6ms. 1-channel - A-phase inductor current 2-channel -A phase 1-tube driver, 3-channel -A phase 2-tube driver, 4-channel -A phase 3-tube driver, 5-channel -A phase 5-tube driver. Could you please check if there is any problem with the timing of this configuration method that causes abnormal wave generation