Hello,
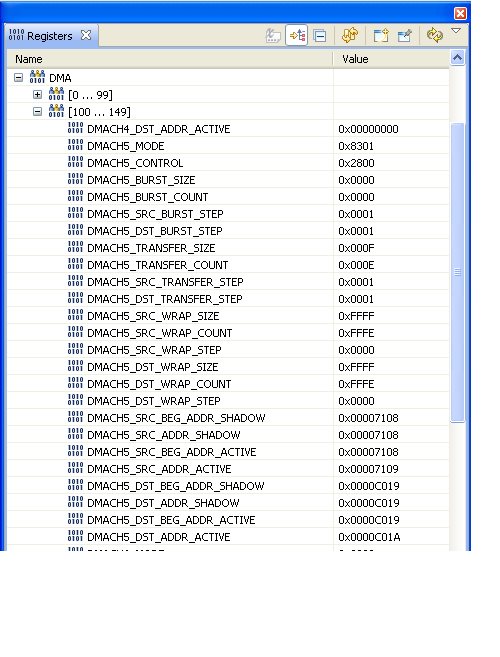
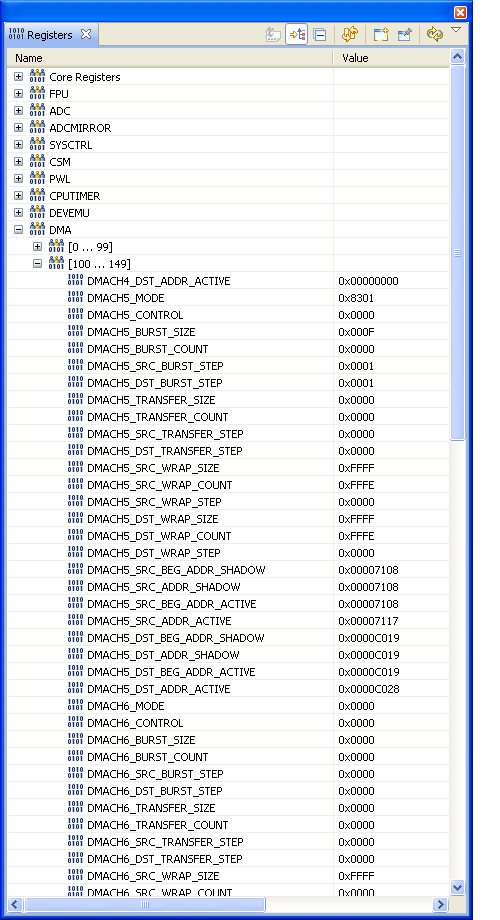
I am confused about how to a cascaded configured ADC with the DMA. I tried all combinations of setting AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 and DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.PERINTSEL. The code below shows the only configuration that allows the DMA to run somewhat, i.e. it only decrements the transfer count by 1 (from 15 to 14). I included the DMA5 register image below.
Why isn't the DMA running to completion?
Stephen
CODE:
int main(void)
{
DisableDog();
InitProcessor();
DMA_Init();
InternalADC_Init();
InternalADC_StartCapture();
while (!InternalADC_DataReady())
{
};
while (1)
{
};
return 0;
}
Uint8 InternalADC_DataReady(void)
{
return ADCdataReady;
}
void InternalADC_StartCapture(void)
{
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.SOC_SEQ1 = 1;
}
void InternalADC_Init(void)
{
Uint16 i;
ADCdataReady = FALSE;
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
InternalADCdata[i]=0;
}
EALLOW;
// HSPCLK to ADC enabled
SysCtrlRegs.PCLKCR0.bit.ADCENCLK = 1;
PieVectTable.DINTCH5 = &InternalADC_DMAwriteTransferComplete_ISR;
EDIS;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.RESET = 1; // Reset the ADC
asm(" RPT #22 || NOP"); // Must wait for ADC reset to take effect
(*ADC_cal_func_ptr)();
//--- Select the ADC reference
AdcRegs.ADCREFSEL.bit.REF_SEL = 0; // 0=internal, 1=external
//--- Power-up the ADC
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.all = 0;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCBGRFDN = 3;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCPWDN = 1; // Power-up reference and main ADC
AdcRegs.ADCTRL3.bit.ADCCLKPS = 13; // ADC Core Clock = HSPCLK/(26*(ADCTRL1[7]+1))
DELAY_US(5000); // Wait 5ms before using the ADC
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.all = 0x0000;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.ACQ_PS = 1;
AdcRegs.ADCTRL1.bit.SEQ_CASC = 1; // Sequencer are cascaded.
//--- Configure the other ADC register
// 16 channels will be converted
AdcRegs.ADCMAXCONV.all = INT_ADC_NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS-1;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV00 = 0;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV01 = 1;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV02 = 2;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ1.bit.CONV03 = 3;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ2.bit.CONV04 = 4;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ2.bit.CONV05 = 5;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ2.bit.CONV06 = 6;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ2.bit.CONV07 = 7;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ3.bit.CONV08 = 8;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ3.bit.CONV09 = 9;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ3.bit.CONV10 = 10;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ3.bit.CONV11 = 11;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ4.bit.CONV12 = 12;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ4.bit.CONV13 = 13;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ4.bit.CONV14 = 14;
AdcRegs.ADCCHSELSEQ4.bit.CONV15 = 15;
#if (INT_ADC_NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS >= 8)
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1;
#elif
AdcRegs.ADCTRL2.bit.INT_ENA_SEQ1 = 1;
#endif
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER7.bit.INTx5 = 1;// Enable PIE Group 7, INT 5 (DMA CH5)
DMAInitialize();
EALLOW;
DmaRegs.CH5.BURST_SIZE.all = 0; // 1 word/burst
DmaRegs.CH5.SRC_BURST_STEP = 1; // increment 1 16-bit addr. btwn words
DmaRegs.CH5.DST_BURST_STEP = 1; // increment 1 16-bit addr. btwn words
DmaRegs.CH5.TRANSFER_SIZE = INT_ADC_NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS-1; // Interrupt every 16 bursts/transfer
DmaRegs.CH5.SRC_TRANSFER_STEP = 1; // Move to next word in buffer after each word in a burst
DmaRegs.CH5.DST_TRANSFER_STEP = 1; // Go back to AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0
DmaRegs.CH5.SRC_ADDR_SHADOW = (Uint32) &AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0;
DmaRegs.CH5.SRC_BEG_ADDR_SHADOW = (Uint32) &AdcRegs.ADCRESULT0;
DmaRegs.CH5.DST_ADDR_SHADOW = (Uint32) &InternalADCdata[0];
DmaRegs.CH5.DST_BEG_ADDR_SHADOW = (Uint32) &InternalADCdata[0];
DmaRegs.CH5.CONTROL.bit.SYNCCLR = 1; // Clear sync flag
DmaRegs.CH5.CONTROL.bit.ERRCLR = 1; // Clear sync error flag
DmaRegs.CH5.DST_WRAP_SIZE = 0xFFFF; // Put to maximum - don't want destination wrap
DmaRegs.CH5.SRC_WRAP_SIZE = 0xFFFF; // Put to maximum - don't want source wrap
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.SYNCE = 0; // No sync signal
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.SYNCSEL = 0; // No sync signal
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.CHINTE = 1; // Enable channel interrupt
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.CHINTMODE = 1; // Interrupt at end of transfer
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.PERINTE = 1; // Enable peripheral interrupt event
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.PERINTSEL = DMA_SEQ1INT; // Peripheral interrupt select = DMA_SEQ1INT
DmaRegs.CH5.CONTROL.bit.PERINTCLR = 1; // Clear any spurious interrupt flags
DmaRegs.CH5.MODE.bit.DATASIZE = 0;
DmaRegs.CH5.CONTROL.bit.RUN = 1;
EDIS;
IER |= M_INT7 ;
}