Hi: all
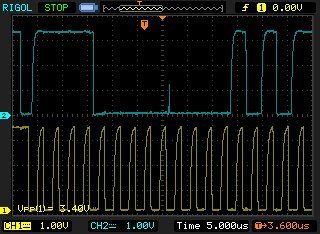
I use 280xx connect eeprom 24c16b (2046byte memory) .but from scoper ,I find eeprom hasn't send ACK bit . it is NACK bit in I2C bus.
my program use consuit I2C-eeprome for 28035. when download to my board. debug. programe can run into i2c_int1a_isr(); but eeprome no respond. I sure eeprome is fine.
this my code and 24c16b datasheet.
where my configuration is wrong?
//###########################################################################
//
//! \addtogroup f2803x_example_list
//! <h1>I2C EEPROM(i2c_eeprom)</h1>
//!
//! This program requires an external I2C EEPROM connected to
//! the I2C bus at address 0x50.
//! This program will write 1-14 words to EEPROM and read them back.
//! The data written and the EEPROM address written to are contained
//! in the message structure, \b I2cMsgOut1. The data read back will be
//! contained in the message structure \b I2cMsgIn1.
//!
//! \note This program will only work on kits that have an on-board I2C EEPROM. T
//! (e.g. F2803x eZdsp)
//!
//! \b Watch \b Variables \n
//! - I2cMsgIn1
//! - I2cMsgOut1
//
//###########################################################################
// $TI Release: F2803x C/C++ Header Files and Peripheral Examples V127 $
// $Release Date: March 30, 2013 $
//###########################################################################
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
// Note: I2C Macros used in this example can be found in the
// DSP2803x_I2C_defines.h file
// Prototype statements for functions found within this file.
void I2CA_Init(void);
Uint16 I2CA_WriteData(struct I2CMSG *msg);
//Uint16 I2CA_WriteData(struct I2CMSG *msg,Uint16 slaveAddress,Uint16 writeNumber);
Uint16 I2CA_ReadData(struct I2CMSG *msg);
//Uint16 I2CA_ReadData(struct I2CMSG *msg,Uint16 slaveAddress,Uint16 readNumber);
__interrupt void i2c_int1a_isr(void);
void pass(void);
void fail(void);
#define I2C_SLAVE_ADDR 0xA40A
#define I2C_NUMBYTES 2
#define I2C_EEPROM_HIGH_ADDR 0x02
#define I2C_EEPROM_LOW_ADDR 0x0A
// Global variables
// Two bytes will be used for the outgoing address,
// thus only setup 14 bytes maximum
struct I2CMSG I2cMsgOut1={I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_WITHSTOP,
I2C_SLAVE_ADDR,
I2C_NUMBYTES,
I2C_EEPROM_HIGH_ADDR,
I2C_EEPROM_LOW_ADDR,
0x12, // Msg Byte 1
0x34}; // Msg Byte 2
struct I2CMSG I2cMsgIn1={ I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP,
I2C_SLAVE_ADDR,
I2C_NUMBYTES,
I2C_EEPROM_HIGH_ADDR,
I2C_EEPROM_LOW_ADDR};
struct I2CMSG *CurrentMsgPtr; // Used in interrupts
Uint16 PassCount;
Uint16 FailCount;
void main(void)
{
Uint16 Error;
Uint16 i;
// Uint16 slaveaddress;
// Uint16 datanumber;
CurrentMsgPtr = &I2cMsgOut1;
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2803x_SysCtrl.c file.
InitSysCtrl();
// Step 2. Initalize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2803x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
// InitGpio();
// Setup only the GP I/O only for I2C functionality
InitI2CGpio();
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table:
// Disable CPU interrupts
DINT;
// Initialize PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2803x_PieCtrl.c file.
InitPieCtrl();
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags:
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2803x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2803x_PieVect.c.
InitPieVectTable();
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers
PieVectTable.I2CINT1A = &i2c_int1a_isr;
EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2803x_InitPeripherals.c
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
I2CA_Init();
// Step 5. User specific code
// Clear Counters
PassCount = 0;
FailCount = 0;
// Clear incoming message buffer
for (i = 0; i < I2C_MAX_BUFFER_SIZE; i++)
{
I2cMsgIn1.MsgBuffer[i] = 0x0000;
}
// Enable interrupts required for this example
// Enable I2C interrupt 1 in the PIE: Group 8 interrupt 1
PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER8.bit.INTx1 = 1;
// Enable CPU INT8 which is connected to PIE group 8
IER |= M_INT8;
EINT;
// Application loop
for(;;)
{
// slaveaddress=522;
// datanumber=1;
//////////////////////////////////
// Write data to EEPROM section //
//////////////////////////////////
// Check the outgoing message to see if it should be sent.
// In this example it is initialized to send with a stop bit.
if(I2cMsgOut1.MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_WITHSTOP)
{
// Error = I2CA_WriteData(&I2cMsgOut1,slaveaddress,datanumber);
Error = I2CA_WriteData(&I2cMsgOut1);
// If communication is correctly initiated, set msg status to busy
// and update CurrentMsgPtr for the interrupt service routine.
// Otherwise, do nothing and try again next loop. Once message is
// initiated, the I2C interrupts will handle the rest. Search for
// i2c_int1a_isr in the i2c_eeprom_isr.c file.
if (Error == I2C_SUCCESS)
{
CurrentMsgPtr = &I2cMsgOut1;
I2cMsgOut1.MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_WRITE_BUSY;
}
} // end of write section
///////////////////////////////////
// Read data from EEPROM section //
///////////////////////////////////
// Check outgoing message status. Bypass read section if status is
// not inactive.
if (I2cMsgOut1.MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_INACTIVE)
{
// Check incoming message status.
if(I2cMsgIn1.MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP)
{
// EEPROM address setup portion
// while(I2CA_ReadData(&I2cMsgIn1,slaveaddress,datanumber)!= I2C_SUCCESS)
while(I2CA_ReadData(&I2cMsgIn1)!= I2C_SUCCESS)
{
// Maybe setup an attempt counter to break an infinite while
// loop. The EEPROM will send back a NACK while it is performing
// a write operation. Even though the write communique is
// complete at this point, the EEPROM could still be busy
// programming the data. Therefore, multiple attempts are
// necessary.
}
// Update current message pointer and message status
CurrentMsgPtr = &I2cMsgIn1;
I2cMsgIn1.MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP_BUSY;
}
// Once message has progressed past setting up the internal address
// of the EEPROM, send a restart to read the data bytes from the
// EEPROM. Complete the communique with a stop bit. MsgStatus is
// updated in the interrupt service routine.
else if(I2cMsgIn1.MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_RESTART)
{
// Read data portion
// while(I2CA_ReadData(&I2cMsgIn1,slaveaddress,datanumber) != I2C_SUCCESS)
while(I2CA_ReadData(&I2cMsgIn1) != I2C_SUCCESS)
{
// Maybe setup an attempt counter to break an infinite while
// loop.
}
// Update current message pointer and message status
CurrentMsgPtr = &I2cMsgIn1;
I2cMsgIn1.MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_READ_BUSY;
}
} // end of read section
} // end of for(;;)
} // end of main
void I2CA_Init(void)
{
// Initialize I2C
I2caRegs.I2CSAR = 0xA000; // Slave address - EEPROM control code
I2caRegs.I2CPSC.all = 6; // Prescaler - need 7-12 Mhz on module clk
I2caRegs.I2CCLKL = 10; // NOTE: must be non zero
I2caRegs.I2CCLKH = 5; // NOTE: must be non zero
I2caRegs.I2CIER.all = 0x24; // Enable SCD & ARDY interrupts
I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x0120; // Take I2C out of reset 10BIT address
// Stop I2C when suspended
I2caRegs.I2CFFTX.all = 0x6000; // Enable FIFO mode and TXFIFO
I2caRegs.I2CFFRX.all = 0x2040; // Enable RXFIFO, clear RXFFINT,
return;
}
Uint16 I2CA_WriteData(struct I2CMSG *msg)
{
Uint16 i;
// Wait until the STP bit is cleared from any previous master communication.
// Clearing of this bit by the module is delayed until after the SCD bit is
// set. If this bit is not checked prior to initiating a new message, the
// I2C could get confused.
if (I2caRegs.I2CMDR.bit.STP == 1)
{
return I2C_STP_NOT_READY_ERROR;
}
// Setup slave address
I2caRegs.I2CSAR = msg->SlaveAddress;
// Check if bus busy
if (I2caRegs.I2CSTR.bit.BB == 1)
{
return I2C_BUS_BUSY_ERROR;
}
// Setup number of bytes to send
// MsgBuffer + Address
I2caRegs.I2CCNT = msg->NumOfBytes+2;
// Setup data to send
I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryHighAddr;
I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryLowAddr;
// for (i=0; i<msg->NumOfBytes-2; i++)
for (i=0; i<msg->NumOfBytes; i++)
{
I2caRegs.I2CDXR = *(msg->MsgBuffer+i);
}
// Send start as master transmitter
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x6E20;
I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x6F20; //10bit
return I2C_SUCCESS;
}
//Uint16 I2CA_WriteData(struct I2CMSG *msg,Uint16 slaveAddress,Uint16 writeNumber)
//{
// Uint16 i;
// Uint16 addresstemple1;
//
//
// // Wait until the STP bit is cleared from any previous master communication.
// // Clearing of this bit by the module is delayed until after the SCD bit is
// // set. If this bit is not checked prior to initiating a new message, the
// // I2C could get confused.
// if (I2caRegs.I2CMDR.bit.STP == 1)
// {
// return I2C_STP_NOT_READY_ERROR;
// }
//
// // Setup slave address
//// I2caRegs.I2CSAR = msg->SlaveAddress;
//
// // Setup slave address+pageAddress
// addresstemple1=0xA0|((slaveAddress>>8)&0x0E);
// I2caRegs.I2CSAR = addresstemple1;
//
// // Check if bus busy
// if (I2caRegs.I2CSTR.bit.BB == 1)
// {
// return I2C_BUS_BUSY_ERROR;
// }
//
// // Setup number of bytes to send
// // MsgBuffer + Address
// // I2caRegs.I2CCNT = msg->NumOfBytes+2;
// I2caRegs.I2CCNT = writeNumber;
//
// // Setup data to send
//// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryHighAddr;
//// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryLowAddr;
//
// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = slaveAddress&0x00ff;
//// for (i=0; i<msg->NumOfBytes-2; i++)
//// for (i=0; i<msg->NumOfBytes; i++)
//
// for(i=0;i<writeNumber;i++)
//
// {
// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = *(msg->MsgBuffer+i);
// }
//
// // Send start as master transmitter
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x6E20; // 0x6E20;
//
//
// return I2C_SUCCESS;
//}
Uint16 I2CA_ReadData(struct I2CMSG *msg)
{
// Wait until the STP bit is cleared from any previous master communication.
// Clearing of this bit by the module is delayed until after the SCD bit is
// set. If this bit is not checked prior to initiating a new message, the
// I2C could get confused.
if (I2caRegs.I2CMDR.bit.STP == 1)
{
return I2C_STP_NOT_READY_ERROR;
}
I2caRegs.I2CSAR = msg->SlaveAddress;
if(msg->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP)
{
// Check if bus busy
if (I2caRegs.I2CSTR.bit.BB == 1)
{
return I2C_BUS_BUSY_ERROR;
}
I2caRegs.I2CCNT = 2;
I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryHighAddr;
I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryLowAddr;
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2620; // Send data to setup EEPROM address
I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2720; //10BIT address
}
else if(msg->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_RESTART)
{
I2caRegs.I2CCNT = msg->NumOfBytes; // Setup how many bytes to expect
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2C20; // Send restart as master receiver
I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2E20; //10BIT address
}
return I2C_SUCCESS;
}
//Uint16 I2CA_ReadData(struct I2CMSG *msg,Uint16 slaveAddress,Uint16 readNumber)
//{
// Uint16 addresstemple2;
// // Wait until the STP bit is cleared from any previous master communication.
// // Clearing of this bit by the module is delayed until after the SCD bit is
// // set. If this bit is not checked prior to initiating a new message, the
// // I2C could get confused.
// if (I2caRegs.I2CMDR.bit.STP == 1)
// {
// return I2C_STP_NOT_READY_ERROR;
// }
// addresstemple2=0xA1|((slaveAddress>>8)&0x0E);
//// I2caRegs.I2CSAR = msg->SlaveAddress;
// I2caRegs.I2CSAR = addresstemple2;
//
// if(msg->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP)
// {
// // Check if bus busy
// if (I2caRegs.I2CSTR.bit.BB == 1)
// {
// return I2C_BUS_BUSY_ERROR;
// }
// I2caRegs.I2CCNT = 1;
//// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryHighAddr;
//// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = msg->MemoryLowAddr;
// I2caRegs.I2CDXR = slaveAddress&0x00ff;
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2620; //0x2620; // Send data to setup EEPROM address
//
// }
// else if(msg->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_RESTART)
// {
//// I2caRegs.I2CCNT = msg->NumOfBytes; // Setup how many bytes to expect
// I2caRegs.I2CCNT = readNumber;
// I2caRegs.I2CMDR.all = 0x2C20; //0x2C20; // Send restart as master receiver
// }
//
// return I2C_SUCCESS;
//}
__interrupt void i2c_int1a_isr(void) // I2C-A
{
Uint16 IntSource, i;
// Read interrupt source
IntSource = I2caRegs.I2CISRC.all;
// Interrupt source = stop condition detected
if(IntSource == I2C_SCD_ISRC)
{
// If completed message was writing data, reset msg to inactive state
if (CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_WRITE_BUSY)
{
CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_INACTIVE;
}
else
{
// If a message receives a NACK during the address setup portion of the
// EEPROM read, the code further below included in the register access ready
// interrupt source code will generate a stop condition. After the stop
// condition is received (here), set the message status to try again.
// User may want to limit the number of retries before generating an error.
if(CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP_BUSY)
{
CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP;
}
// If completed message was reading EEPROM data, reset msg to inactive state
// and read data from FIFO.
else if (CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_READ_BUSY)
{
CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_INACTIVE;
for(i=0; i < I2C_NUMBYTES; i++)
{
CurrentMsgPtr->MsgBuffer[i] = I2caRegs.I2CDRR;
}
{
// Check received data
for(i=0; i < I2C_NUMBYTES; i++)
{
if(I2cMsgIn1.MsgBuffer[i] == I2cMsgOut1.MsgBuffer[i])
{
PassCount++;
}
else
{
FailCount++;
}
}
if(PassCount == I2C_NUMBYTES)
{
pass();
}
else
{
fail();
}
}
}
}
} // end of stop condition detected
// Interrupt source = Register Access Ready
// This interrupt is used to determine when the EEPROM address setup portion of the
// read data communication is complete. Since no stop bit is commanded, this flag
// tells us when the message has been sent instead of the SCD flag. If a NACK is
// received, clear the NACK bit and command a stop. Otherwise, move on to the read
// data portion of the communication.
else if(IntSource == I2C_ARDY_ISRC)
{
if(I2caRegs.I2CSTR.bit.NACK == 1)
{
I2caRegs.I2CMDR.bit.STP = 1;
I2caRegs.I2CSTR.all = I2C_CLR_NACK_BIT;
}
else if(CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus == I2C_MSGSTAT_SEND_NOSTOP_BUSY)
{
CurrentMsgPtr->MsgStatus = I2C_MSGSTAT_RESTART;
}
} // end of register access ready
else
{
// Generate some error due to invalid interrupt source
__asm(" ESTOP0");
}
// Enable future I2C (PIE Group 8) interrupts
PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP8;
}
void pass()
{
__asm(" ESTOP0");
for(;;);
}
void fail()
{
__asm(" ESTOP0");
for(;;);
}
//===========================================================================
// No more.
//===========================================================================
best regard!
YZ