Hi,
I am trying interface eeprom 24c02 IC using I2C with F28069.I want to write multiple Write byte constructively and want to read random address read and Multiple read byte opearation.
I am using sample code of I2C_eeprom of F28069 for write 2 byte on 0x0001 and 0x0002 memory add. location and also read same location. after read I get same data which is i write on 0x0002.
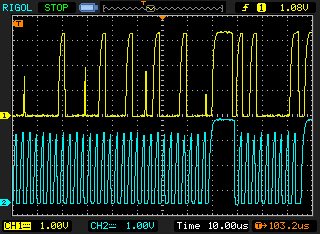
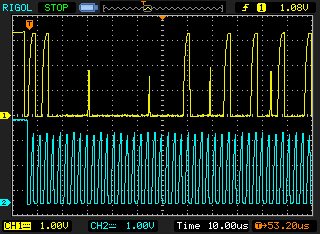
Please find attached waveform which I captured foe 2 byte write operation.
From which I knew only first data has been written.
Please help me for write multiple write data.
Regards,
Sagar