Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE,
Tool/software: Code Composer Studio
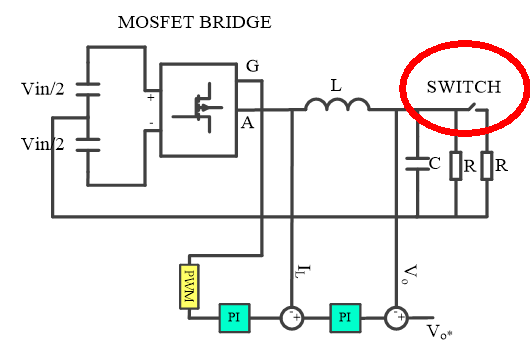
Hello,
I have simulated half bridge single phase inverter dual loop outer is voltage loop and inner is current loop with 50Khz switching frequency low power with Vin = 50V and Vo is 15V , Rload is 10ohm and neutral point is connected in between two DC link capacitors(VDC_link= Vin/2 compensator formulla in my simulation is P(1=ITs.1/z-1) and forward Euler integrator method. my simulation working fine, output voltage and current are right. I set KP and KI according to Hit and error method(for current loop Kp=0.05 and KI=6000 upper and lower limits are 15 and -15 respectively and for voltage loop KP= 5 and KI =500, upper and lower limits are 3 and -3 repectively ) . After that i have made hardware circuit according to my simulation. i used TMS320F2837xD Dual-Core Delfino™ Microcontrollers, I have written c code in code composer studio V8.2. and i have used Solar library provided by TI in which i used PID_GRANDO. I set derivative term zero and i put same KP and KI paramaters of my simulation in current and voltage loop but it does not work output of both PI contoller are same as their limits and fixed. could you tell me why is that or i can not used solar lib? do i need other library ? could you please send me some document or any software which can tune PI parameters for single phase inverters. thanks