Hello,
I am a student working on a senior design project utilizing the Tiva tm4c123gh6pm arm processor and am struggling to get the SPI slave interface to work correctly.
So far I have used an example from this form post, https://e2e.ti.com/support/microcontrollers/tiva_arm/f/908/t/302734?SPI-Slave-problem
and modified it to use SSI0 instead of SSI2. When testing the code I cannot read more than one byte from the master, a raspberry pi, before the Tiva hangs in an infinite loop in the function SSIDataGet() shown below waiting for data. The master has the clock set to 122kHz.
void
SSIDataGet(uint32_t ui32Base, uint32_t *pui32Data)
{
//
// Check the arguments.
//
ASSERT(_SSIBaseValid(ui32Base));
//
// Wait until there is data to be read.
//
while(!(HWREG(ui32Base + SSI_O_SR) & SSI_SR_RNE)) // hangs here forever
{
}
//
// Read data from SSI.
//
*pui32Data = HWREG(ui32Base + SSI_O_DR);
}
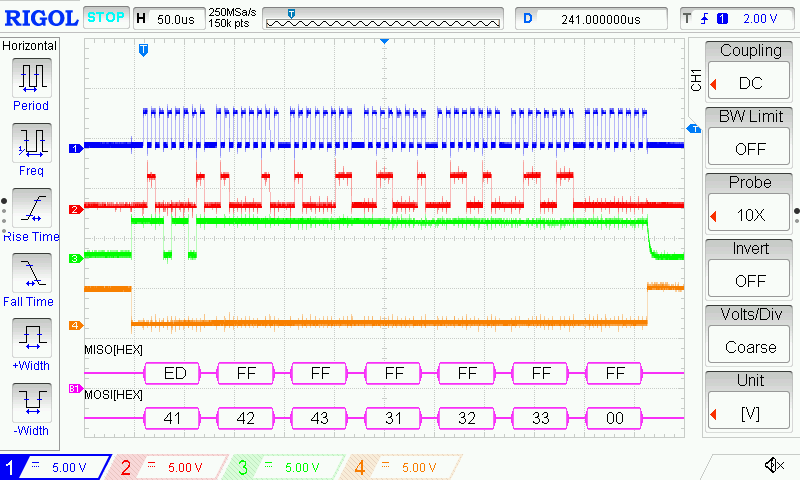
The oscilloscope output shows the data as being sent correctly but it seems it is not being processed by the Tiva and I am unsure as how to fix this.
Channel 1 is clk, 2 is MOSI, 3 is MISO, 4 is CS.
Any advice would be greatly appreciated, here is my full code below.
//*****************************************************************************
//
// spi_slave.c - Example demonstrating how to configure RX timeout interrupt in
// SPI slave mode.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// TI Information - Selective Disclosure
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_ssi.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/ssi.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "utils/uartstdio.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup ssi_examples_list
//! <h1>SPI Slave (spi_slave)</h1>
//!
//! This example configures the SSI0 as SPI Master, SSI2 as SPI Slave on an
//! EK-LM4F232 evaluation board. RX timeout interrupt is configured for SSI2.
//! Three characters are sent on the master TX, then SSI2 RX timeout interrupt
//! is enabled. The code then waits for the interrupt to fire. Once the
//! interrupt is fired the data from slave RX FIFO is read and compared to the
//! transmitted packet and the appropriate status is displayed. If everything
//! goes well you should see a "Test Passed." message on the terminal window.
//! The status messages are transmitted over UART0 at 115200 baud and 8-n-1
//! mode.
//!
//! This example uses the following peripherals and I/O signals on EK-LM4F232.
//! You must review these and change as needed for your own board:
//! - SSI0 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port A peripheral (for SSI0 pins) (available near the SD card slot)
//! - SSI0CLK - PA2
//! - SSI0Fss - PA3
//! - SSI0Rx - PA4
//! - SSI0Tx - PA5
//!
//! - SSI2 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port M peripheral (for SSI2 pins) (available right below the OLED)
//! - SSI2CLK - PH4
//! - SSI2Fss - PH5
//! - SSI2Rx - PH6
//! - SSI2Tx - PH7
//!
//! For this example to work, the following connections are needed on the
//! EK-LM4F232 evaluation board.
//! - SSI0CLK(PA2) - SSI2CLK(PH4)
//! - SSI0Fss(PA3) - SSI0Fss(PH5)
//! - SSI0Rx(PA4) - SSI2Tx(PH7)
//! - SSI0Tx(PA5) - SSI2Rx(PH6)
//!
//! The following UART signals are configured only for displaying console
//! messages for this example. These are not required for operation of SSI0.
//! - UART0 peripheral
//! - GPIO Port A peripheral (for UART0 pins)
//! - UART0RX - PA0
//! - UART0TX - PA1
//!
//! This example uses the following interrupt handlers. To use this example
//! in your own application you must add these interrupt handlers to your
//! vector table.
//! - SSI2IntHandler.
//!
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Number of bytes to send and receive.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#define NUM_SSI_DATA 7
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Global variables used in interrupt handler and the main loop.
//
//*****************************************************************************
volatile unsigned long g_ulSSI0RXTO = 0;
unsigned long g_ulDataRx0[NUM_SSI_DATA] = {0};
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Interrupt handler for SSI0 peripheral in slave mode. It reads the interrupt
// status and if the interrupt is fired by a RX time out interrupt it reads the
// SSI0 RX FIFO and increments a counter to tell the main loop that RX timeout
// interrupt was fired.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
SSI0IntHandler(void)
{
unsigned long ulStatus = 0, ulIndex = 0;
//
// Read interrupt status.
//
ulStatus = SSIIntStatus(SSI0_BASE, 0);
//
// Check the reason for the interrupt.
//
if(ulStatus & SSI_RXTO)
{
//
// Interrupt is because of RX time out. So increment counter to tell
// main loop that RX timeout interrupt occurred.
//
g_ulSSI0RXTO++;
//
// Read NUM_SSI_DATA bytes of data from SSI2 RX FIFO.
//
for(int ulIndex = 0; ulIndex < NUM_SSI_DATA; ulIndex++){
SSIDataGet(SSI0_BASE, &g_ulDataRx0[ulIndex]);
}
}
//
// Clear interrupts.
//
SSIIntClear(SSI0_BASE, ulStatus);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This function sets up SPI0 to be used as Master in freescale mode.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
InitSPI0(void)
{
//
// The SSI0 peripheral must be enabled for use.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_SSI0);
//
// For this example SSI0 is used with PortA[5:2]. GPIO port A needs to be
// enabled so these pins can be used.
//
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
//
// Configure the pin muxing for SSI0 functions on port A2, A3, A4, and A5.
// This step is not necessary if your part does not support pin muxing.
//
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0RX);
GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0TX);
//
// Configure the GPIO settings for the SSI pins. This function also gives
// control of these pins to the SSI hardware. Consult the data sheet to
// see which functions are allocated per pin.
// The pins are assigned as follows:
// PA5 - SSI0Tx
// PA4 - SSI0Rx
// PA3 - SSI0Fss
// PA2 - SSI0CLK
//
GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_2);
//
// Configure and enable the SSI0 port for SPI slave mode.
//
SSIConfigSetExpClk(SSI0_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), SSI_FRF_MOTO_MODE_0,
SSI_MODE_SLAVE, 122000, 8);
//
// Enable the SSI0 module.
//
SSIEnable(SSI0_BASE);
}
int main(void)
{
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_1 | SYSCTL_USE_OSC | SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ);
InitSPI0();
SSIDataPut(SSI0_BASE, 0xED);
// rx interrupt
SSIIntEnable(SSI0_BASE, SSI_RXTO);
IntEnable(INT_SSI0);
while(1); // debug halt here and check buffer
}