1. When the motor is rotating, IN1 and IN2 are input high at the same time to make the motor brake, but the motor will not brake as expected. At this time, the FAULTn pin can be detected to be pulled low.
2. When the chip is in the initial state where IN1 and IN2 input high at the same time, pull down one of the pins and the motor will not start. Only when the initial state is IN1 and IN2 input low at the same time, pull up one of the pins to make the motor rotate.
3. If you connect the ISENSE pin directly to ground, and try to start the motor at this time, the motor cannot start, and the FAULTn pin can be detected to be pulled low.
4. When the IN1 and IN2 inputs are one high and one low during the normal control of the motor rotation, there is a certain probability that the motor will stop abnormally. Use an oscilloscope to test that the IN1 and IN2 inputs have no change, but OUT1 and OUT2 no longer output voltage. And this phenomenon will only appear in a certain direction of rotation of the motor, instead of rotating in both directions, the motor may stop abnormally. When the motor stops abnormally, the FAULTn pin may output low, or it may still be in a high impedance state.
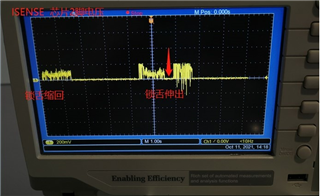
1. DRV8832 drives the bolt, and the bolt is retracted during the current reliability test. The rotation is normal, and no problems are found;
The bolt will stop abnormally when the bolt is stretched out, as indicated by the following waveform arrow, stop rotating, and then the software detects the fault low level, then pulls up the fault, IN1/IN2 is set to 0, and then IN1/IN2 is driven by 1, 0
In this way, the lock tongue extension process stops abnormally and always exists. After the machine run for about tens of thousands of times, the entire lock tongue will appear to be incompletely extended. As the running time is longer, the probability of the lock tongue being incompletely extended increases.
please help confirm
1. The reason for the abnormal stop of the bolt extension;
2. After run the machine for a period of time, the reason for the decrease of the motor drive capacity;