Hi,
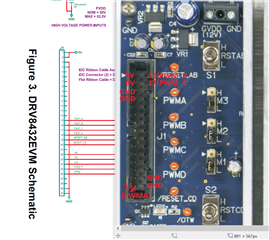
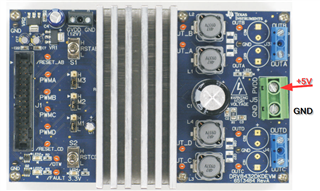
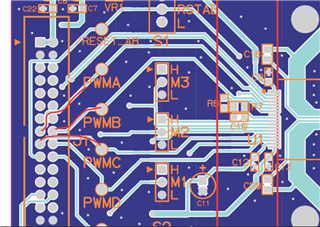
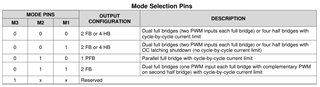
I want to drive a brushless motor using the drv8432dkdevm, but couldn't find out, which pins I have to use for the PWM-signals.
Therefore I searched for the manual of the drv8432dkdevm, but I didn't find it anywhere.
Where can I download it ?
(I need to add a part number here in the forum, but it does only accept the DRV8434AEVM. But I want to use the DRV8432AEVM)
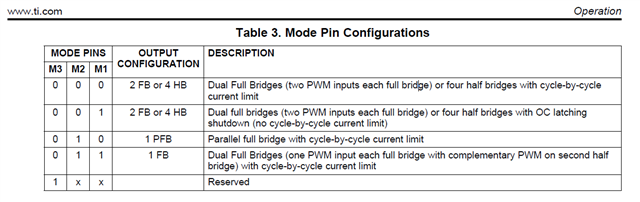
And do I need to send the PWM-signal AND the inverted signal to drive the motor ? Or only the pwm-signal ?
thanks,