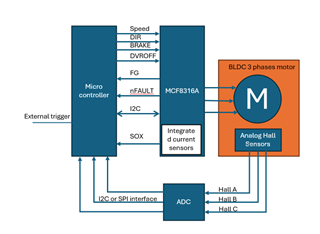
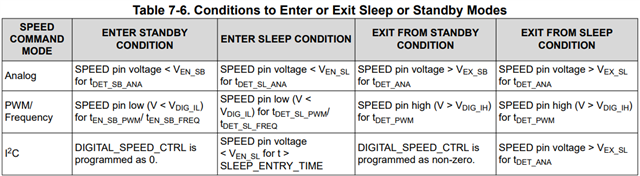
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: MCT8316Z,
Tool/software:
Hello expert
I am researching the MCF8316A for my motor control project. The motor has a maximum torque of 11mNm and a maximum acceleration of 204,000 rad/s^2. With MCF8316A, Can I control the motor to rotate 17 degrees in 1.8ms and then brake the motor with high side braking and can the motor stop before an angle of 19 degrees? . Is the align brake function suitable for my needs?
Note : J_total = 1.99*10^(-8)
Thank you expert. Have a nice day.