Other Parts Discussed in Thread: DRV8703-Q1,
Tool/software:
Hey,
I'm working on a development project that involves the DRV8703. I'm pretty new to Motor Drivers and Motors, and I'm a bit confused about the Terminology.
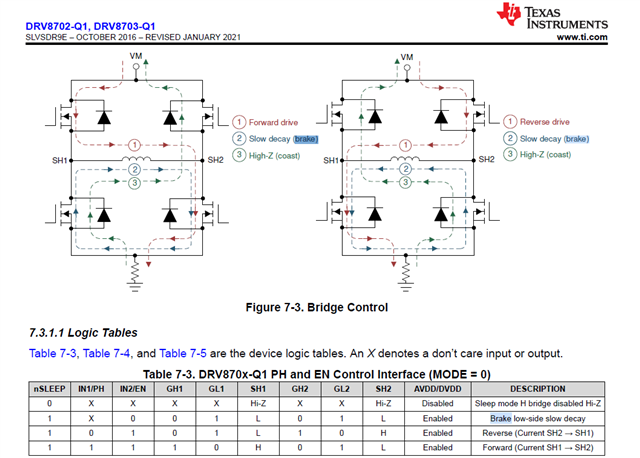
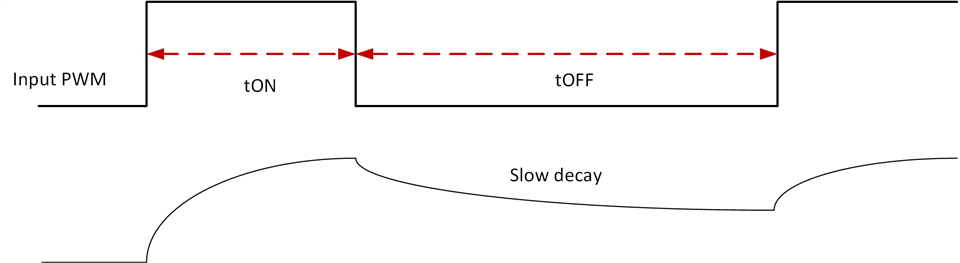
The Data sheet talks about a Slow Decay (Brake). Other Forum post like this one:
Speak about a passive Breaking. Is this the same case for this Motor Driver?
To be exact, that it will stop the Motor from moving with its current PWM but won't provide much Resistance to outside forces trying to turn the motor in this "brake" state?
Or the power/efficiency of the Brake low-side slow decay can't be compared to a disc brake on a bike.