Tool/software:
Hello,
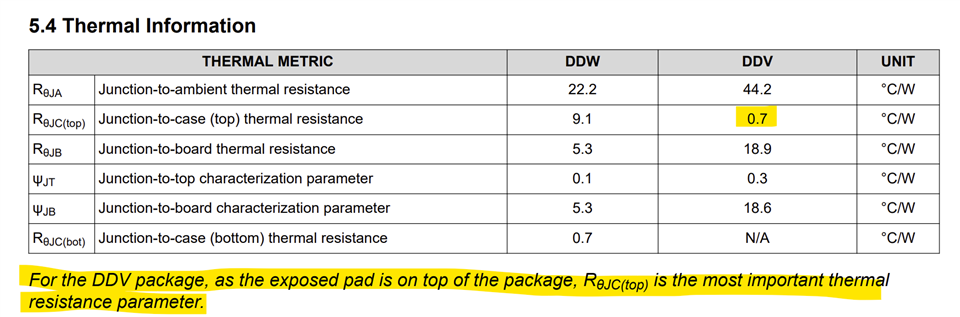
I know that there is DDV package for DRV8262 and its EVM with a big heatsink.
Dose this EVM (DRV8262 DDV package) use of heatsink as main source of dissipating the heat? I was initially thinking of using DDW package and I know that its EVM does not require heatsink as it uses copper layer of PCB to dissipate the thermal dissipation (please correct me if I am misunderstanding). If I want to dissipate the heat properly and be able to drive about 5A at DC by using single H-bridge to drive brushed DC motor, how smaller can PCB possibly be sized? I know DDW package has been simulated with a certain size of copper (around 110mm x 80mm) without heatsink. Is it possible to design with 50mm x 50mm (either with DDV or DDW) of PCB with an external heatsink assuming that I have enough room for adding heatsink? Or would it be possible to design for my application (5A DC) with higher PCB layer count, for example, 6 layer or 8 layers if necessary. I currently don't have thermal simulation tool with me so It's hard to anticipate the result, but I wanted to see feasibility before proceeding with the design.
Thanks