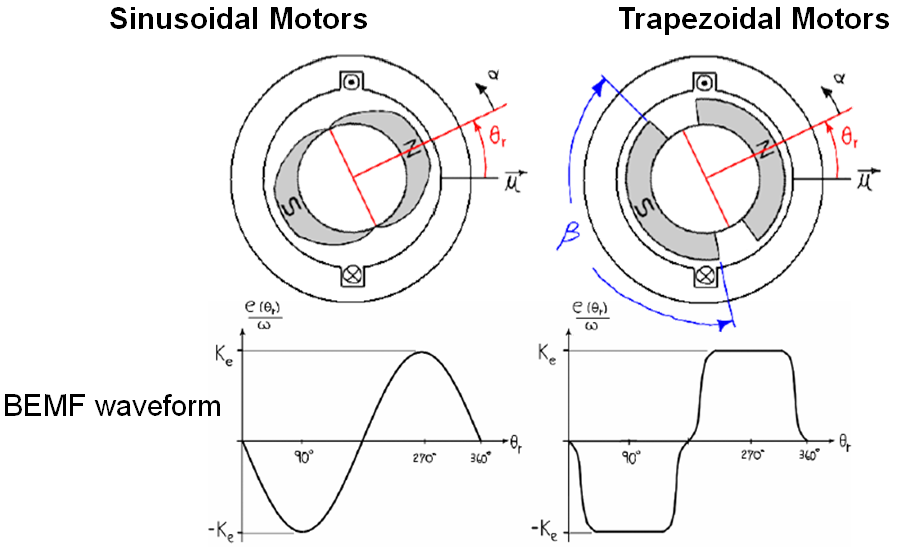
Brushless DC motors fall into one of two categories. either Trapezoidal or Sinusoidal. This distinction refers to the Back Electromotive Force (Back-EMF) of the motor and is created through the type of winding and magnets used in each style of motor.
Trapezoidal motors are often referred to simply as BLDC motors while sinusoidal motors are usually referred to as PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor). Some features and benefits of each motor type are listed below:
|
|
Trap |
Sine |
|
Torque Ripple |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Peak Torque |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Power Density |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Phases Driven per commutation cycle |
2 |
3 |
|
Commutation simplicity |
More |
Less |
|
Low RPM performance |
Worse |
Better |
|
Noise and Vibration |
Worse |
Better |
Trapezoidal motors can be driven with Sinusoidal commutation, vice-versa sinusoidal motors can be driven with trapezoidal commutation. The most efficient way to drive a motor of either type is to match the commutation style to the motor winding style.
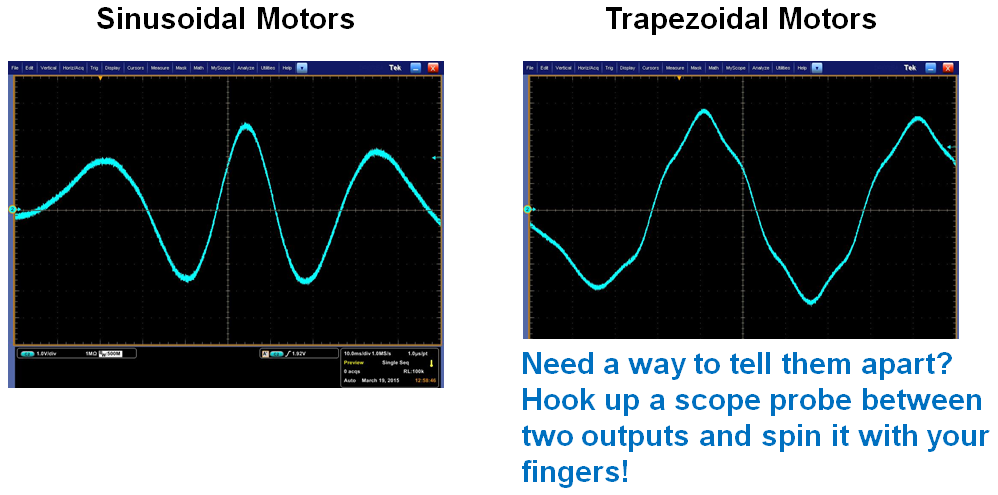
The motor datasheet should list the BEMF or winding style. If it is not mentioned, the BEMF can be measured using a scope connecting from one phase to another and spinning the motor by hand. A resulting waveform resembling one of the two shown below should be seen:
Regards,
-Adam