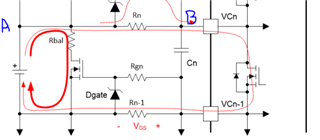
The app note SLUAA81 says:
A Zener diode is needed to protect the external FET gate from pack transients. For example, in the event of a
short across the pack in a 10-cell battery, Cell 10 would have approximately 40V across R n during the event and
the opposite transient at the release of the short circuit. The gate voltage should be connected through a resistor
to limit the current when the diode conducts.
I am trying to understand the reason for transients on Gate. please explain how come the voltage be 40V across Rn during short circuit event ?Lets say Point A is 40V but why point B voltage will drop ?
Please help.