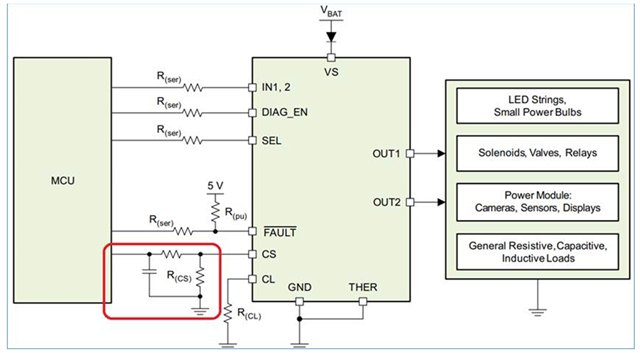
Hi Team
We have discussed the same topic before! (See E2E link below)
Now there are new questions that need your help ,THX
>>>Because according to the description in the datasheet, Channel ON does not need to pull up 20K ohms.
Although FAULT will not be output, the MCU can still detect it through other settings.
Is this narrative as we understand it?
If so, how should it be implemented?