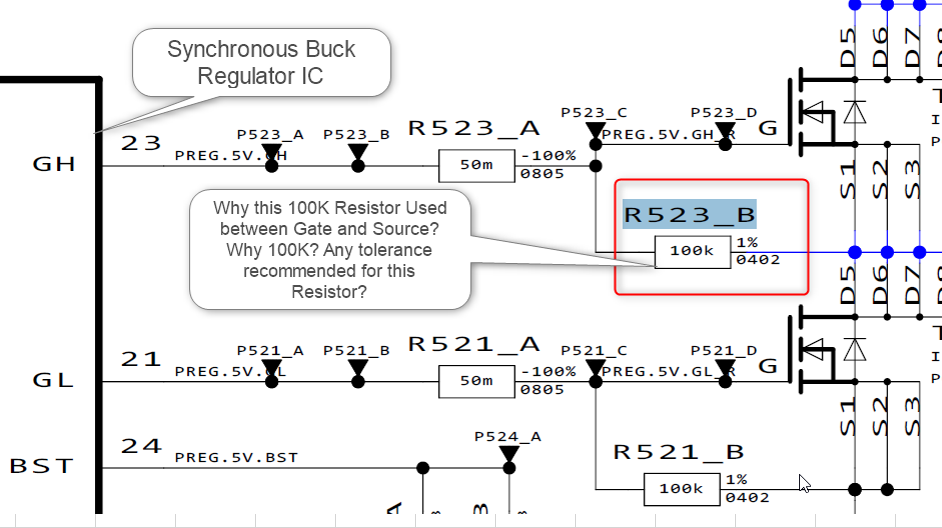
Why this 100K Resistor Used between Gate and Source?
Why 100K? Any tolerance recommended for this Resistor?
What is the significance of this Resistor (R523_B) used between Gate and Source of N channel MOSFET. in synchronous Buck converter application.
Do we have any application note on this?

