Hi team,
I have a question. What is the difference between common source or common drain? In my understanding, both topology seems to be the same.
Best Regards,
Shoji
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Hi team,
I have a question. What is the difference between common source or common drain? In my understanding, both topology seems to be the same.
Best Regards,
Shoji
Hi Shoji,
The FETs orientation is the difference in common source and common drain topology.
In common drain topology, the ideal diode FET is connected at the input and the load switch FET is connected at the output. So, the common drain point is an Always ON node as the ideal diode FET will conduct even when the FET is turned OFF for Vin > Vout.
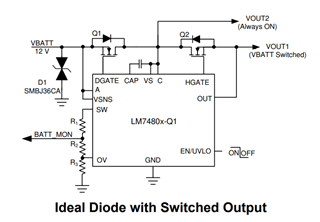
In common source topology, the load switch FET is connected at the input and the ideal diode FET is connected at the output. This topology is suitable for applications where the input surge/transient voltage can go beyond the Abs Max rating of 70V (like 200V Unsuppressed Load Dump).
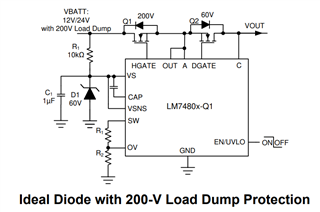
Hi Praveen,
Apologies for my delay.
So, is the difference between both topology surge capability and on-timing on the mid point?
Regarding parasitic diode direction, both- topology can achieve reverse polarity protection and reverse current protection, right?
Best Regards,
Shoji
Hi Shoji,
CS topology provides surge protection which is not supported by CD topology.
CD topology has a always Always ON node which is protected from input reverse polarity. This is not available in CS topology.
Yes, both topologies can provide reverse polarity protection and reverse current blocking functionalities.