Hello,
I plan to make a design with TL494. But here I could not understand the high wattage values of the resistors connected to the output pins. What is the reason for this?
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Hello,
I plan to make a design with TL494. But here I could not understand the high wattage values of the resistors connected to the output pins. What is the reason for this?

Enes,
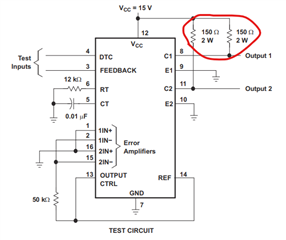
The circuit you are showing is a parametric test circuit. The high power rating resistors are only required to test at the parametric corners specified in the data sheet. For example, the VCE(sat) is ~1.1V and VCC is 15V. 15V-1.1V=13.9V across the collector pullup resistor means there is (13.9V)^2/150Ω=1.29W dissipation in the resistor which is why the resistor is rated 2W.
Regards,
Steve
I actually don't understand this. Will two output pins in my applications consume that much power?
Because I will feed this integrated with the aux winding of the transformer. I think it will not be able to provide such high power values.
I am thinking of connecting the output pins directly to the gate pin of the mosfet with a gate resistor without connecting them to Vcc. Would this be a mistake?
Enes,
No, the two output pins in your switching converter application should not consume much power at all. Again, the circuit you referenced is a parametric test circuit intended to test the max continuous collector current. In a switching converter application, you are likely driving one or two external power MOSFETs switching the primary side of a transformer. The peak current required by the power MOSFET is high but short duration and the average current, determined by switching frequency, is comparatively small.
The internal bipolar transistors of the TL494 output stage are not intended to drive the external power MOSFETs directly. The TL494 provides the gate drive logic signals which are then used as input signals to an external gate drive circuit. The external gate drive circuit is providing the high peak source/sink current needed to efficiently drive the external power MOSFETs. The TL494 output current is rated for 200mA source/sink current but a gate drive peak source/sink current rating should be more like ±1Apk.
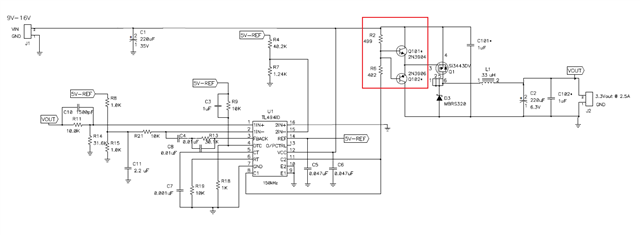
Below is an example of TL494 buck converter and you can see the external totem pole gate drive circuit (red box) used to drive MOSFET, Q1. If your prefer not to design the external gate drive circuit discretely, check out TI's extensive portfolio of integrated gate driver ICs here.
Regards,
Steve
Okay, I got it. Thanks.
I will share the schematic of thehalf bridge application I am trying to make with you when I finish.
So can you share a half bridge application schematic with me as an example?
Enes,
I believe your inquiry about the power rating of the C1 and C2 resistors has been resolved. As such, I am going to close this thread but if you need additional support, please feel free to open a new E2E thread.
Regards,
Steve