Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TIDA-010247
Dears,
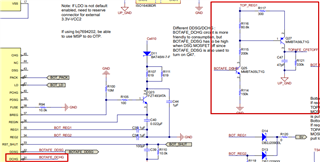
We refer to TIDA-010247 to do 2pcs AFE stack design to meet the requirements of 24-string battery applications;
TIDA-010247 can only be directly controlled by the High AFE, and cannot be directly controlled by the Low AFE. As a result, TIDA-010247 cannot immediately control the N-MOSFET when it detects a fault, resulting in delay.
We need advice on how to design the external circuit so that low AFE can directly control the N-MOSFET instead of reporting errors to the MCU or High AFE via I2C.