Other Parts Discussed in Thread: TPS92641, TPS922054
Tool/software:
Hello guys,
One of my customers is considering using TPS922052 to their new products.
At this moment, they have the following questions.
Could you please give me your reply?
Q1.
It is important for them that the delay time from PWM signal input to LED turning on/off completely.
The complete LED turning on means that LED current reaches target current. And complete LED turning off means that LED current becomes zero.
Could you tell me how to calculate the delay time under Vin=24V, LED total Vf=20V and If=2A conditions?
I think the delay time would be changed by inductor value.
Could you please give me how to calculate the inductor value under same conditions?
Q2.
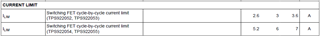
What is TPS922052 maximum average drive current? Is it more than 2A?
If PWM signal on duty is limited less than 70%, 50% or 30%, can the maximum average drive current be increased?
Q3.
Can shunt FET LED on/off method like TPS92641 be used for TPS922052?
Q4.
Do you have any LED driver which can turns LED on/off with us level delay time under conditions above except TPS922052 family and TPS92641?
Your reply would be much appreciated.
Best regards,
Kazuya.