Other Parts Discussed in Thread: UCC29002
Tool/software:
Hi Team,
Could you please help explain how this device works? Are there any slides or ANs you can share?
Regards,
Hailiang
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
Hello Hailiang,
Aside from the information within the UCC29002 datasheet, there are several App Notes and help files listed in the UCC29002 product folder, here: https://www.ti.com/product/UCC39002#tech-docs
Please peruse these.
Regards,
Ulrich
Hi Ulrich,
1. If two power supplies are connected in parallel and one power supply has no output due to a fault, can the other power supply work? What will be the behavior of the load sharing IC at this time?
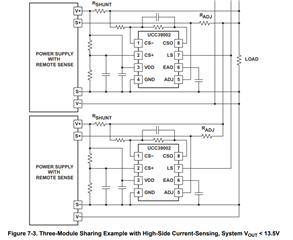
Regards,
Hailiang
Hello Hailiang,
If two power supplies are normally sharing the current 50/50 to a single load, then if one supply fails, the other supply can still work normally if it is capable of supplying 100% of the load current. It must be assumed that the failure mode cannot overload the common Vout bus.
Let us assume that each power supply can individually deliver at least 100% of the maximum load current. Then, during normal sharing they split the current roughly 50/50. It does not matter which load-share controller is the leader and which is the follower. The sharing will be roughly equal.
Suppose the top supply fails; then its output current goes to zero and its current-sense voltage goes to zero. The current-amplifier output will be lower than the load-share (LS) bus voltage and the load-share controller for the failed PSU will maximize its ADJ current to attempt to increase Vout of its corresponding failed PSU to provide more current, but that will be unsuccessful (since the PSU has failed).
Meanwhile, the remaining bottom supply will experience a load step to 100% load current. It will experience a transient Vout drop and recover according to its normal transient response. Because its current has increased, its corresponding load-share controller will automatically become the load-share leader and drive the load-share bus (LS bus) higher, but will not affect the Vout feedback of the working PSU.
Regards,
Ulrich