Other Parts Discussed in Thread: , UCD3138064
Tool/software:
I am writing some code to allow the UCD3138128A to be programmed though a serial port.
The question I have is
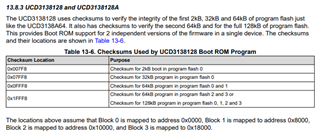
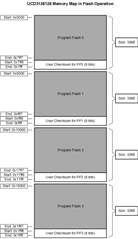
What do I have to do to make the boot code recognize an image in blocks 2 and 3 to switch too when it boots up.
And then.. how to I get it to switch to blocks 0 and 1 again when I program those with a newer image?