Tool/software:
Hi Team,
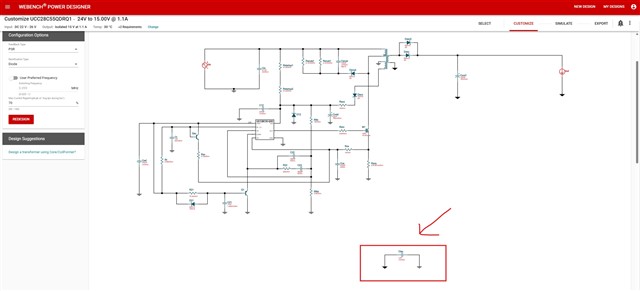
I am designing an isolated DC-DC flyback converter using the UCC28C55-Q1 IC (schematics attached). The Webench Power Designer suggests including an isolation capacitor between the primary and secondary grounds, but I couldn't find specific details about its role.
Could you kindly clarify the following:
-
How does this isolation capacitor affect the overall isolation between the primary and secondary sides? For example, if I use a transformer rated for 5kV but the capacitor is only 2kV, does this compromise isolation integrity?
-
What impact would omitting this capacitor have on electromagnetic interference (EMI) performance?
Any information or resources on this subject would be greatly appreciated.
Best regards,

