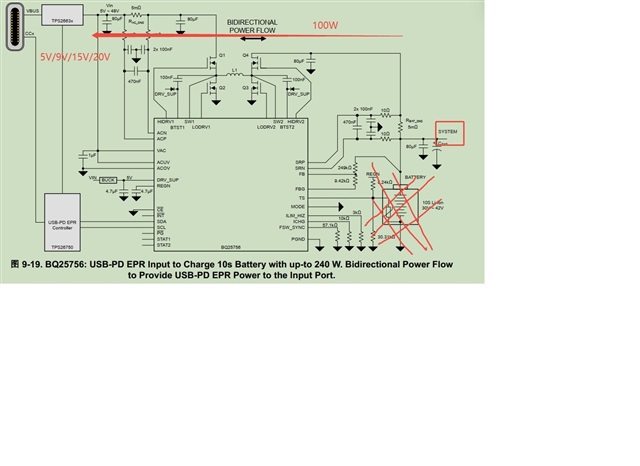
Other Parts Discussed in Thread: BQ25756, , PMP41083
Tool/software:
Hi
Project background: The customer's battery is powered by other chargers, and the battery can be plugged in and out. TYPE-C is not required to power the battery. The maximum external discharge power of TYPE-C is 100W. Based on my current understanding of the BQ25756 and TPS25751 specifications and the PMP41083 reference design, I have the following questions:
1. The current application is the system---->type-c in the figure below. I would like to ask, how do I adjust the input voltage of the TYPE-C device I inserted? That is, how is Vout (VBUS) switched? (My idea is that the back-end device communicates with PD through CC, and then PD uses I2C to adjust the output voltage of BQ25756. I wonder if my idea is correct? If it is correct, is there a more detailed answer?)
2. In typical applications and reference circuits, we will not use the battery in the figure. If so, can BQ25756 still work normally?
3. If the above conditions cannot make BQ25756 work properly, please recommend a buck-boost controller that can be paired with TPS25751
. Thank you