Dear Support,
I see strange behaviour when reading out the Data Flash.
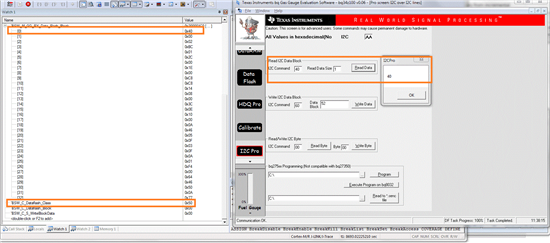
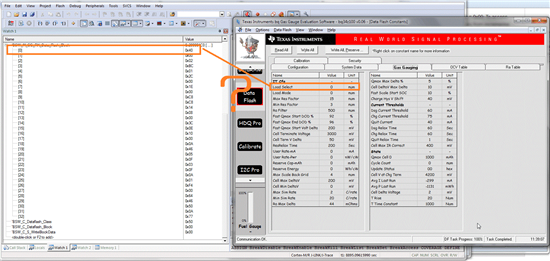
Please see the screenshots below. What I'd like to show is an example from reading Subclass 80 (0x50) aka. IT Cfg.
Data Flash Class is set to 0x50, Offset is set to 0.
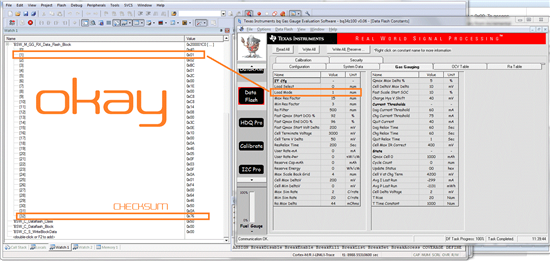
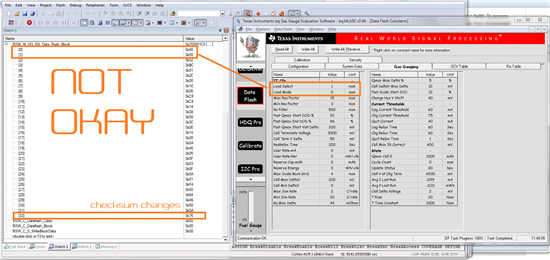
You see 33 bytes that where read from the gasgauge (32 bytes + Checksum byte). The first byte does not react on changes, made by the EVM Software (when manipulating "Load Select", but the Checksum updates correctly.
The second byte "Load Mode" reacts to changes correctly, means that when I change the Value of Load Mode via the EVM software, I see the changing bit also in the debugger of my MCU.
I verified, that reading from address 0x40 (start of Data Flash Block) gives the same result in the EVM-software (i2C-read).
I even tried the same software on a second EVM-module I bought, but I get the same strange behaviout. I am out of ideas! Need help urgently! Thanks a lot