Hi team
My customer designed the circuit with reference to PWR758.
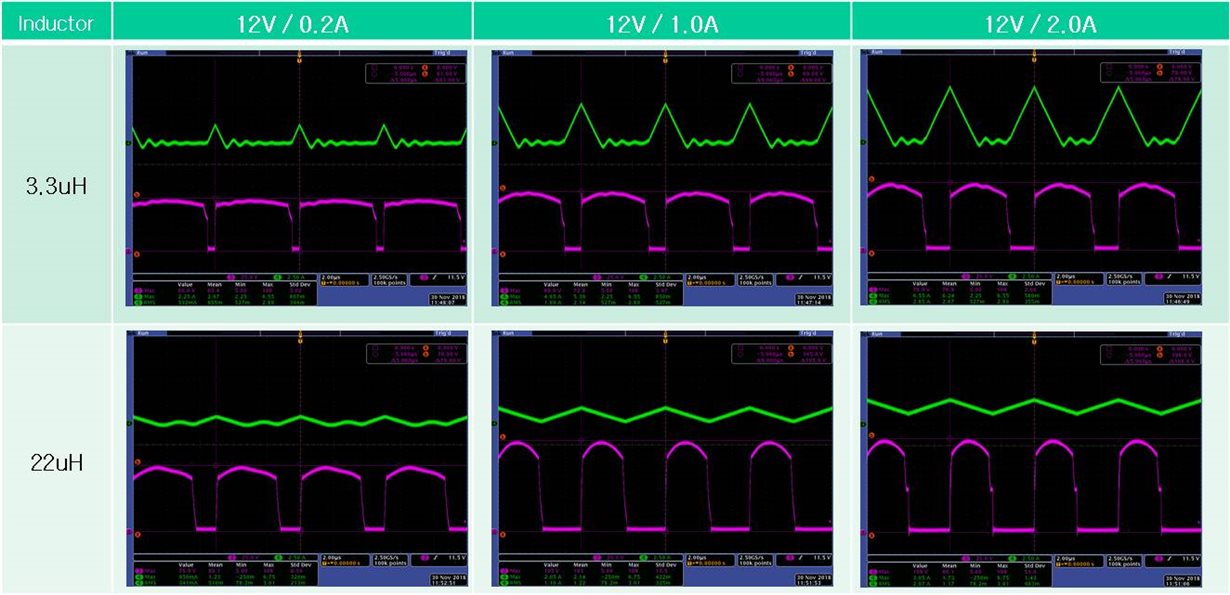
Increasing the output load as shown below changes the Vds value of the switching FET.
- Pink : Vds(Switching voltage for FET) / Green : Inductor Current
The PWR758 EVM does not change the switching voltage(Vds) even when the output load varies.
When the output inductor is subjected to aging test with 22uH applied, the transformer generates heat and a switching oscillation occurs.
The circuit diagram and each measurement point are shown below.:
The pin map of the transformer is different using the circuit library I used.
Please refer to the following for transformer information.
Please check and reply the following :
1. Why the Vds of the UCC2897A FET changes when the output inductor is changed?
2. Is it normal for FET Vds to change with load variation?
3. Is it normal for switching duty to change with load variation?
4. What is the cause of transformer heat generation and FET oscillation?