Hello,
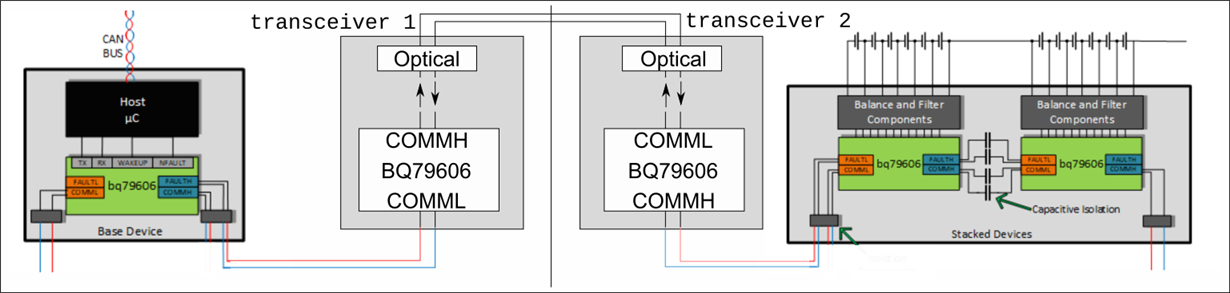
I’m designing an optical transceiver for the BQ79606’s COMM Daisy Chain Bus and would like to ask a few questions regarding the use of the BQ79606 as an electrical interface chip.
Is it possible to configure the BQ79606 in a way that it only functions as an interface chip without participating (listening / responding to the data) on the bus? Ideally the BQ79606 would behave completely transparently so no changes to an existing bus would be needed when an optical transceiver is added.
As an alternative to using the BQ79606, does TI offer a dedicated interface IC for the COMM Bus?
Best Regards
Achim